Hyperbranched polymers are one of the hot research topics in the field of polymers in recent years. Due to their special structure, properties and potential application prospects, this kind of polymers has attracted widespread attention from the scientific and industrial circles. Hyperbranched polymers have low melt viscosity, solubility and many modifiable end groups, which determine that hyperbranched polymers will be widely used in the field of coatings. Hyperbranched polymer-based resins are more effective than those with linear unsaturated Resin has lower viscosity and higher cure rate. Hyperbranched polyester and acrylic acid copolymers can be used in UV-curable coatings. Without any photosensitizer, it can reduce the cost of UV-curable coatings by 10% to 40%, making hyperbranched polyester and its modified copolymers research is favored. Hyperbranched polymers have been made into photocurable coating resins, which can greatly improve the cost performance of coating products. In the field of coatings, the most widely studied hyperbranched polymers are currently commercialized hyperbranched fatty polyester Boltorne and hyperbranched polyesteramine Hybranee. Using hyperbranched polymers in alkyd resin paint formulations, it was found that compared with traditional alkyd resins with similar molecular weight, acid value and hydroxyl value, hyperbranched polymers have low viscosity, fast drying and strong outdoor weather resistance At the same time, it can increase the reactivity and reduce the viscosity, and shorten the drying time, so that the coating can have a higher solid content when the viscosity is applied. In the previous research, the author modified the alkyd resin with a hyperbranched polymer whose terminal group is hydroxyl, which helps to improve the transparency and flexibility of the paint film.
The author studied the application of the synthesized hyperbranched resin in matte topcoat, and investigated its matting performance. The study found that although the hyperbranched resin modified with fatty acid has poor matting property, the transparency and impact resistance of the paint film can be improved by partially replacing the commercial matte resin with it.
1 Experimental part
1.1 Raw materials
p-toluenesulfonic acid: analytically pure, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Company; pentaerythritol: industrial grade, Sweden; trimethylolpropane: industrial grade, Sweden; octapentyl glycol: industrial grade, domestic; dimethylolpropionic acid (DMPA): Industrial grade, Sweden; Phthalic anhydride: Industrial grade, domestic; Lauric acid: Industrial grade, domestic; Synthetic fatty acid: Industrial grade, Japan; Butyl acetate: Industrial grade, domestic; Xylene: Industrial grade , made in CHINA.
1.2 Instrument analysis
Hardness Tester: manufactured by BYK Gardner, Germany; QuaNix 1500 metal coating Thickness Gauge: manufactured by Nix, Germany; paint film adhesion Tester: DFZ-Ⅱ, manufactured by CHINA Tianjin Material Testing Machine Factory; QCJ type paint film impact Instrument: manufactured by Tianjin Material Testing Machine Factory, CHINA; gloss meter: WGG60-E, manufactured by Keshijia Optical Instrument Research Institute; QTX paint film elasticity Tester: manufactured by Tianjin Zhonghuan Testing Instrument Factory.
1.3 Synthesis of hyperbranched resin
The synthesis method of matrix hyperbranched polymers can be found in reference [6]. Put matrix hyperbranched polymer, fatty acid, phthalic anhydride and other monomers into the reactor according to a certain ratio, then gradually raise the temperature to 200 °C, use xylene as the reflux solvent, after a certain period of reaction, detect the acid value of the reaction mixture, when After the acid value reaches a certain value, the temperature is lowered, and the resin is diluted to a certain solid content with butyl acetate, and finally discharged to obtain a butyl acetate solution of the hyperbranched resin. Its principle is shown in Figure 1.
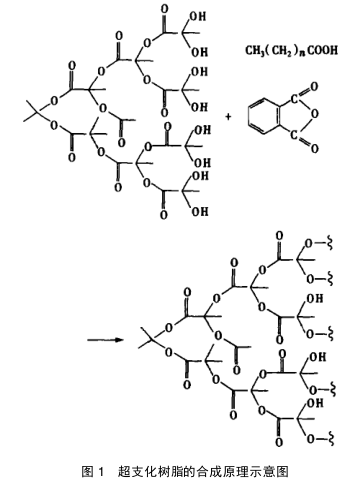
1.4 Basic properties of hyperbranched resins
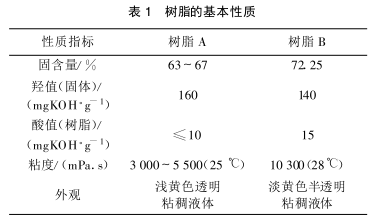
Table 1 lists the basic physical properties of the commercial resin A and the synthesized hyperbranched resin B.
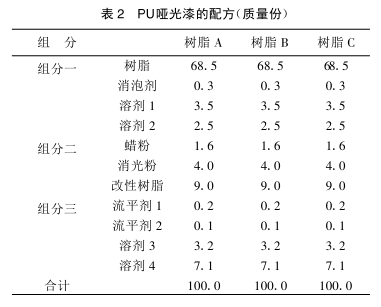
1.5 Formulation design of paint
Table 2 is the paint formulation design. The formula design principle is to ensure that their solid content is the same for comparison. Resin C is a mixed resin of commercial resin A and hyperbranched resin B, and the mixing ratio is m(A):m(B)=8:2.
2 Results and discussion
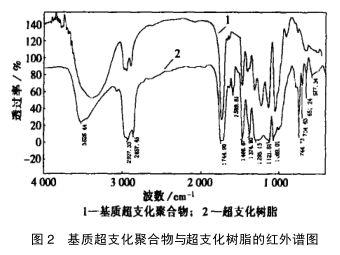
2.1 Infrared spectrum analysis of matrix hyperbranched polymer and hyperbranched resin
图 2 是基质超支化聚合物与超支化树脂的红外谱图。图中波数为 1 744.90 cm -1 处的吸收峰是酯基的特征吸收峰, 波数为 2 927.33 cm-1 处的吸收峰是由亚甲基伸缩振动的特征吸收峰,在波数为3379.62cm-1 附近出现的很强吸收峰是羟基的特征吸收峰,因为羟基既是氢键的受体又是氢键的给体,聚酯的羟基均位于链的末端,这些末端羟基很容易形成分子内氢键, 从而导致 3 379.62 cm -1 附近出现很强吸收峰。在超支化树脂的红外谱图上该峰的位置不但出现了偏移,位于 3 526.44 cm -1 ,而且可以看出羟基峰的强度已大大减弱,一方面是基质超支化聚合物的羟基被一部分脂肪酸所中和,另一方面是其它基团的作用阻止了分子内氢键的形成。
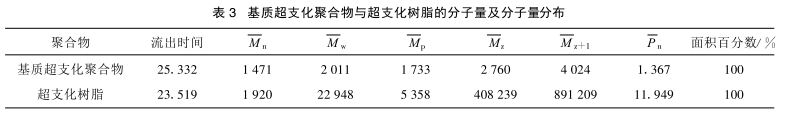
2.2 基质超支化聚合物与超支化树脂的分子量及分子量分布
基质超支化聚合物与超支化树脂的分子量及分子量分布如表 3 所示 。从表 3 流出时间来看,超支化树脂比基质超支化聚合物早出峰 ,说明它的分子量比基质超支化聚合物的分子量大 ,这一结果也体现在它们的数均分子量(M n )和重均分子量(M w )的差别上。从表 3 中还可以看出, 超支化树脂的分散性指数为 11 .949,比基质超支化聚合物的分散性指数(1.367)大,说明它的分子量分布比基质超支化聚合物宽。
2.3 基质超支化聚合物与超支化树脂的玻璃化温度
利用 DSC 对基质超支化聚合物与超支化树脂进行差热分析 ,它们的玻璃化温度如表 4所示。从表 4 中可以看出 :超支化树脂的玻璃化温度较之基质超支化聚合物大大降低 。事实上超支化树脂在常温下是液态, 与通常的溶剂相溶 ;而基质超支化聚合物在常温下是固体, 与一般的极性溶剂不相溶。
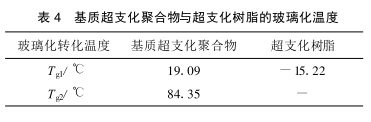
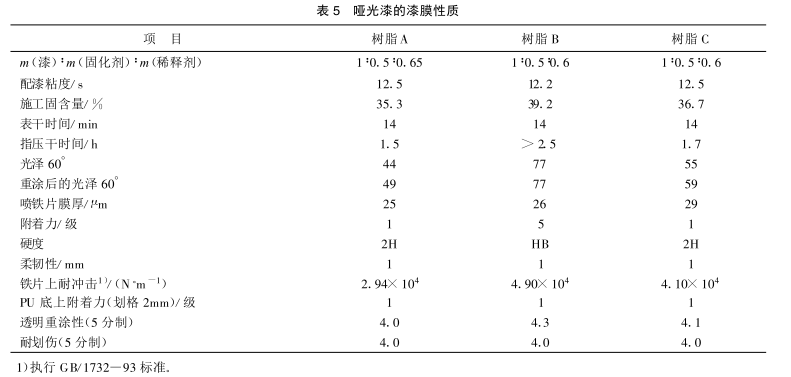
Table 5 lists the film properties of matt paints formulated from commercial resin A and hyperbranched resin B. Film-forming conditions: temperature is 28°C, air humidity is 66%, with TDI trimer curing agent, m(NCO)/m(OH)=0.9, and the substrate is black substrate. From the properties listed in Table 5, it can be seen that compared with the matt paint prepared by commercial resin, the matt paint prepared by hyperbranched resin has the advantages of high solid content in construction and good transparent recoatability. The disadvantage is that the matting property is not as good as that of commercial resins, the adhesion on the iron sheet is poor, the drying is slow, and the hardness is low. Resin C is a mixed resin with a mass fraction of 20% hyperbranched resin B added to commercial resin A. Most of the properties of the matt paint prepared by it are equivalent to the film properties of commercial resin A, and the solid content in construction is Increased, transparent recoatability has improved.
2.4 Comparison of paint film properties
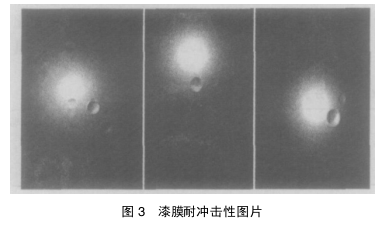
2.5 Impact resistance of paint film
Figure 3 is a picture of the impact resistance of the matte paint on the board, and the picture was taken with a Sony digital camera. From left to right are the impact resistance results of paint film A (commercial resin A), paint film B (hyperbranched resin B) and paint film C (resin C). The depression in Figure 3 is left by the bullet impact test. It can be seen from Figure 3 that the paint film A not only has depressions, but also has a circle of obvious cracks around the depressions, which is the result of the rupture of the paint film after being impacted. However, paint film B and paint film C only left depressions after being subjected to the same impact, and there was no crack phenomenon, and the paint film was not broken. This shows that the impact resistance of paint film B and paint film C is better than that of paint film A.
3 Conclusion
Hyperbranched resins can be synthesized using matrix hyperbranched polymers and monomers such as fatty acids. When it is applied in the matt finish paint, the transparent recoating and impact resistance of the paint film are better than the commercial resins used, but the gloss is too high and the matting property of the resin is poor, so the hyperbranched resin is not suitable for direct use as Matting resin used. Partial modification of commercial resins with hyperbranched resins can improve the transparent recoatability and impact resistance of paint films in matte topcoats.









