Electrophoretic coatings are water-insoluble coating resins that become water-soluble and water-dispersible liquid coatings . Neutralizers (see table), alkaline (OH - ) substances for anodic electrocoating and acidic (-COOH) substances for cathodic electrocoating . Nowadays, cathodic electrophoretic coating with excellent corrosion resistance is the mainstream, so cathodic electrophoretic coating will be introduced . Cathodic electrophoretic coatings are made of water-soluble (water-emulsified) cationic coating particles made of organic acids neutralized with basic resin (ammonia)-based modified epoxy resins and applied to negative polarity coatings. On the surface of the object to be coated, the negative charge is precipitated and the acid becomes insoluble . As this process proceeds, the film will continue to thicken to form a wet coating film until the resistance of the wet coating film is so large that the power is terminated and it is almost no longer coated. Acidic paint particles ionize to become alkaline, and condense on the surface of the object to be coated to form a water-insoluble coating film.
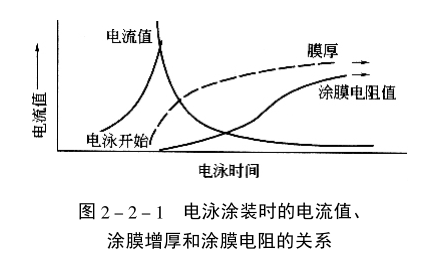
The figure shows the relationship between the current value, the thickness of the coating film, and the resistance of the coating film during electrophoretic coating. The difference between the wet electrophoretic coating and the electroplating layer is that it has a certain resistance value, so it has better swimming power. The composition and function of cathodic electrophoretic coatings and the changes in composition during film formation are listed in the table.
