During oven drying, hot air is blown onto the substrate through nozzles. The heat transfer process is shown in Figure 1, the heat is transferred to the ink side through the thermal boundary layer
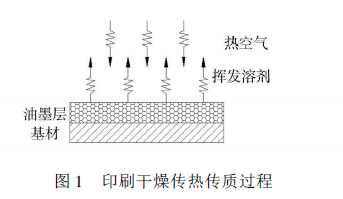
At the substrate interface, the solvent in the ink is evaporated on the surface of the substrate, and the evaporated solvent penetrates and evaporates to the outside of the ink layer through the hollow medium pores. Heat is transferred in the form of latent heat, while some heat is transferred through the solid to the other side in the form of heat conduction. Finally the heat is carried out of the substrate by the air. Due to the transfer of heat, there is a temperature difference on both sides at the same time.
During the gravure printing drying process, the solvent is vaporized on the surface of the material and diffused inside the material at the same time. In the process of hot air convection, heat is transferred from the hot air to the surface of the wet material; at the same time, the steam evaporated from the surface of the wet material together with the enthalpy of the liquid itself is transferred to the flowing air and taken out of the dryer by the air. Due to the evaporation of the solvent , the internal solvent continuously migrates to the surface of the material, and the heat is continuously transferred from the surface of the material to the interior of the material. The heat transfer and mass transfer are carried out simultaneously.
The calculation of the heat and mass transfer process in the drying process can be solved by establishing an effective drying model and using numerical methods. By establishing a drying model, predict the drying rate, temperature and false drying phenomenon caused by "skinning" during the drying process.
1.1 Model analysis of gravure printing drying process
Drying is a dehumidification process accompanied by heat and mass transfer. The moisture in the material obtains heat and becomes steam to be separated from it, and finally a dry product with a low moisture content and meeting a certain requirement is obtained. No matter which drying medium is used, the mechanism of its change during the drying process is the same. It is not only the carrier of heat, but also can take the moisture volatilized out of the dryer.
The gravure oven drying model is shown in Figure 2. The drying medium is air, and the water in the dry printed matter is the drying object. The quantity of printed products is G, the water content requirements before and after drying are w1, w2, fresh air (its state is ambient temperature t0, humidity H0, heat enthalpy I0, dry air volume L) enters the heat exchanger , and after heating (its state is t1, H1, I1, L) into the Drying Oven, the printed product is heated and dried by hot air in the oven , the moisture content is reduced from w1 to w2, and the temperature is raised from tm1 to tm2 and then sent out of the oven; the temperature drops, After the humidity increases, it is discharged from the dryer (its state t2, H2, I2, L); the energy loss of the oven is QL.
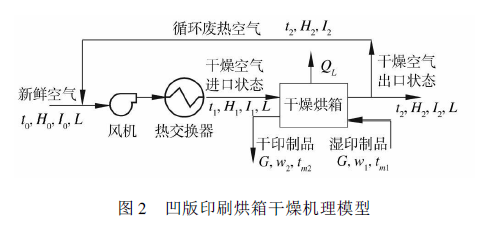
From the dry air inlet state to the outlet state in Figure 1, the air takes the moisture of the printed product inside the oven out of the oven, and the moisture content of the air increases from H1 to H2; at the same time, due to the heat in the air being partially transferred to the printed product , the outlet temperature drops from the original inlet temperature t1 to t2, part of this part of energy is used to heat the printed product, making its temperature rise from tm1 to tm2, and the other part is lost in heat dissipation. Therefore, to improve the energy utilization rate and make the oven achieve energy saving effect, the following measures can be taken:
1) Determine the drying area (solvent volatilization area) and curing area (solvent-free area) of the oven, effectively use the heat energy in the curing area, and realize the secondary recycling of hot air exhaust gas .
2) Recycle the heat of the exhaust gas to reduce the energy .
3) Thermal insulation of the drying system to reduce the energy loss of the drying system.
4) Improve the energy utilization rate of the equipment and reduce the waste of mechanical energy .
1.2 Engineering analysis of drying process
The application of oven drying on printing equipment is very important, especially when designing and manufacturing high-speed printing machines, the design of the drying system is very important. Therefore, it is necessary to combine the drying theory to guide the oven design .
A domestic printing equipment manufacturing company has developed and designed a drying system auxiliary design simulation software on oven drying, as shown in Figure 3. Through the simulation analysis of the software, it is possible to intuitively understand the drying condition of the substrate inside the oven and guide the oven design. This drying system simulation software selects appropriate design parameters such as hot air temperature, wind speed, distance between nozzle and substrate, distance between nozzles, etc. . The software optimizes and analyzes the selected data through the internal drying model, and obtains the simulation data curve through scientific calculation. The data results can simultaneously display the wet bulb temperature of the solvent, the heat transfer system, the latent heat of evaporation, the evaporation amount, and the discharge LEL value.
In the simulation diagram of Fig. 3, the substrate temperature changes from the inlet to the outlet

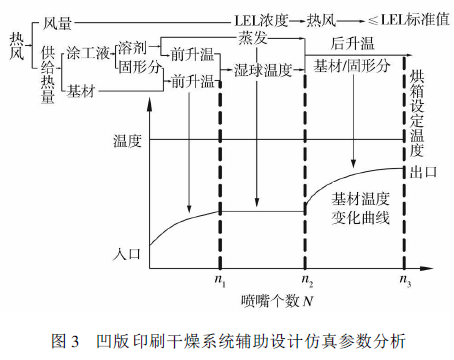
Curve, above which is the oven setting temperature line. It can be seen that when the substrate enters from the oven inlet, the temperature of the substrate, solvent and solid content gradually rises, and when it reaches the nozzle n1, the substrate reaches the wet bulb temperature. This stage belongs to the pre-heating stage, and the drying rate of the substrate gradually increases to the maximum value; the stage from nozzle n1 to nozzle n2 belongs to the constant-speed drying stage, the temperature of the substrate is constant, the drying rate reaches the maximum and constant, and the solvent volatilization in this stage is the largest ; when it reaches the nozzle n2 period, the substrate is completely dry, Afterwards, the substrate heats up rapidly to close to the set temperature of the oven, and then exits the oven. Each stage of the drying process can be clearly observed from the figure , which has an intuitive guiding significance for the design of the oven. For example, when the substrate reaches the nozzle n2, the solvent of the substrate ink is completely volatilized; thereafter, in the , the residual amount of solvent is very small, and the hot air in this section can
All are used for secondary recycling, which is convenient for the oven to save energy.






