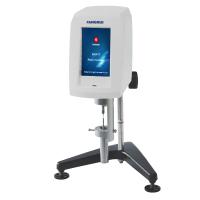
There are many instruments available. Rheometers are capable of accurately measuring viscosity. wide shear stress. The plastic decoration industry usually uses simpler equipment. As mentioned earlier, perhaps a common device is the Brookfield viscometer, where the motor is coupled to the immersion spindle via a tensiometer. The spindle rotates in the liquid to be measured. The higher the viscosity (resistance to flow) the greater.
Tonometer. Several spindle diameters are available, and a number of rotational speeds can be selected. Viscosity needs to be reported as a function of spindle size, RPM and temperature.

The liquid is at 25°C, and the specific gravity of the liquid is about 1 second.
Brookfield instruments are an excellent tool for quality control. While certainly not a replacement rheometer, a viscometer can be used to estimate changes in viscosity versus shear. Viscosity readings at different RPMs and comparisons. Highly thixotropic materials will be easily identifiable. A simpler viscosity device is the Flow Cup, a simple container with an opening at the bottom. Ford Cups and Zane Cups are very common in the field of plastic painting. The Ford Cup, the more accurate of the two, is the stand of support. Once filled, the bottom is an opening to record when the liquid comes out. Unlike Brookfield, which produces a viscosity value, the cup only flows once. Relative flow times reflect different relative viscosities. Conversion charts allow Ford and other cup values to be converted to centipoise (Table 1.2).
The Zahn cup is dipped into the liquid sample by its handle and withdrawn quickly, so the empty time is recorded. Equipment of the Zahn type is commonly used in the field, primarily as a device for examining familiar material.