Surface chemistry is the science that studies the interface of two materials. Interfaces may exist between any form of matter, including gas phases. To understand the interfacial decorative liquid-material interaction, we only need to analyze the liquid-solid interaction. Although there are surface interactions between the liquid coating and the surrounding air, the effect is small. may be overlooked.
1.3.1 Surface tension
All liquids are microscopic assemblies of molecules made of atoms (very few liquids are made of simple atoms). All molecules that are close to each other are attractive. It is these mutual attractions that create what is known as surface tension. Unit Force per unit length: dynes/cm.
A drop of liquid suspended in space quickly assumes a spherical shape. When surface molecules are pulled toward those directly below them, the smallest surface area (sphere) results. The spherical shape is the result of an uneven force distribution; molecules inside the droplet are attracted from all directions, while those on the surface are only pulled towards those below. All liquids try to form a minimal sphere. Some headwinds came into play, however. A liquid placed on a solid provides a liquid-solid interface. This type of interface is very important for plastic decorators because liquid molecules are attracted not only to each other (intramolecular attraction), but to any solid as well. The surfaces they touch (intermolecular attraction). We only need to care about ourselves. There are two kinds of interactions: intramolecular and intermolecular interactions. A basic understanding of this interface interaction will allow decorators to optimize materials and workmanship.
1.3.2 Surface tension measurement
Every liquid has a specific surface tension value. Liquids with high surface tension, such as water (73 dynes/cm), exhibit high intramolecular attractions and a strong tendency (to form beaded balls ). Low value liquids have a weak tendency to sphere formation which is easily overcome. By confronting forces. There are various methods for measuring the surface tension of liquids. Table 1.3 gives the commonly used solvents. The method can also be used to determine the surface tension of solids, usually the surface tension of solids. called surface energy. Table 1.4 gives the surface energy values of plastics. We need only focus on methods for estimating surface tension and techniques for determining relative differences.
1.3.3 Wetting
Liquids placed on a flat, level solid surface are wetted and flow out, otherwise they will dewet to form hemispherical drops. It can also occur between states when the fluid does not subside or progresses but remains static. The angle formed by a drop or edge of a liquid with a solid plane is called the contact angle (Figure 1.4). A non-wetting condition exists when the contact angle is greater than 0°—this is, when the angle is measured— by the method. The attractive forces within the molecules of a liquid are stronger than those on the surface of a solid. This liquid surface tension value is higher than the solid surface energy. The wetting condition occurs at a contact angle of 0°. The edge of the liquid keeps going, albeit perhaps at a slow rate.


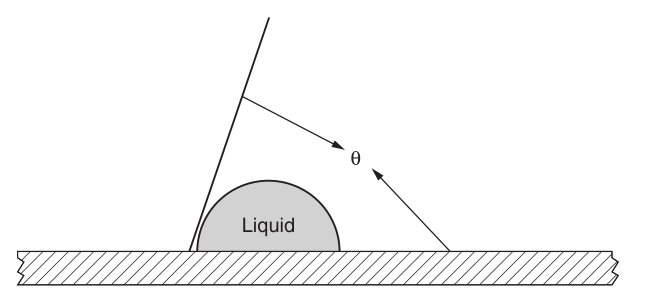
Figure 1.4 Contact Angle

We can estimate the surface tension of a liquid by dropping it onto a known smooth surface. Until wetting occurs, indicating that the two surface tensions are equal. Instead, the surface energy of the solid can be estimated by using a standard surface tension liquid. Wetting is achieved. Surface tension kits can consist of simple mixtures that are used to test surfaces. surface
provide formula
低能量表面很难湿润,在涂料、油漆和印刷方面效果不佳。标准表面张力套件可用来估计待装饰塑料的表面能。如果特定的塑料显示的值比表1.4所列的低得多,则污染是怀疑。脱模剂,除非特别适合装饰材料,可以大大。一个塑料部分较低的表面能,使其uncoatable。
1.3.4表面活性剂
改变界面相互作用的物质称为表面活性剂。表面活性剂有两种不同的化学基团,一种与待修饰的液体相容,另一种具有较低的表面。紧张.例如,环氧树脂的表面张力可以通过加入表面活性剂而降低。酒精组(环氧兼容)一端的含氟组。酒精组将环氧树脂与关联,呈现不含氟的“尾巴”的表面。这个环氧涂层会表现得好像它是一个表面张力低氟。增加一个小的表面活性剂的数量将使环氧涂层难以潮湿,低能量表面,甚至油—污染的塑料。
表面活性剂能有效降低油墨、涂料和油漆的表面张力。通常,1%或更少是足够的。当发生去由于基体的固有的低表面能,使用表面活性剂也称为润湿剂。这些材料不是好房子的替代品—保持和适当的零件准备。污染会导致粘结失效。含氟化合物、有机硅、表面活性剂和碳氢化合物是常见的类别。含氟化合物具有最低的表面张力的任何材料,是有效的润湿剂。有机硅其次是功效,成本更低。然而,某些类型的硅可以变成空气,导致基质污染。
虽然降低涂层的表面张力可能是可取的,但是基底.有助于装饰材料的基材使基材无用。硅胶展—污染会产生臭名昭著的去湿的缺陷称为“鱼眼”。表面活性剂改性的涂料、涂料和油墨通常会长久性地改变,甚至固化后。它们的低表面能将使它们很难被弄湿,例如,它是必要的。涂上面漆。克服这个问题有几种选择。很好的做法是使用最少的有效的表面活性剂来完成这项工作。从烃类开始。还要确保基板是干净的开始。另一种可能性是使用反应性表面活性剂。具有反应能力的官能团的试剂固化后涂层或粘合剂的活性降低。一旦表面活性剂完成了作用润湿剂不再需要了。另一种方法是在第二种材料中加入表面活性剂。适用。通常相同的表面活性剂会起作用,特别是在稍高的负荷下。
1.3.5流平
整平取决于流变学和表面化学。这是一个更复杂的现象。难以控制。喷涂、浸涂、辊涂和其它方法都适用于涂层。往往不够流畅,不适合审美情趣。飞溅,运行,山脊,和其他拓扑缺陷的需要液体物质的水平。因此,了解水准测量的动态是很重要的。我们将首先假定适当润湿,如果必要的润湿剂。重要影响调平的参数是粘度、表面张力、屈服值、涂层厚度和程度。湿法涂布不匀率。一些工人已经发展了描述水准测量的经验关系。水准方程(方程式1.4)非常有用。

at=涂层脊的振幅(高度)
σ=表面张力涂层
η=涂料粘度
h=涂层厚度或高度
t=流平时间
λ=波长或脊之间的距离
方程1.4表明,水准测量是由以下一个或多个改进的:
1.更长的时间(t)
2.涂层表面张力较高(σ)
3.低粘度(η)
4.涂层厚度(h)
5.小的重复距离垄间(λ)
Note that H, the coating thickness, increases to a third power. Doubling the thickness provides eight (2 of 3) increased levels. Note also that λ, the ridge between the wavelengths, is raised to the fourth power. This means that ridges that are far apart create very difficult levels. Earlier, it was pointed out that the value of high yields could prevent levelling. Wet shear stress coatings need to be greater than the yield value for leveling. Equation 1.5 shows the relationship between various parameters and shear stress.

σ = surface tension coating
a = amplitude of coating ridge
h = coating height
λ = Tuling wavelength
Since Equation 1.5 deals with force, time factor and viscosity values drop. It can be seen that increasing the surface tension and coating thickness produces the maximum shear stress. Height of Coating Defect
(a) Shear increases while wavelength (λ) decreases strongly. If coating ridges cannot be avoided, taller, tighter packs are preferable. Leveling does not occur when the yield value is greater than the maximum shear (t) maximum. Extending the leveling time and lowering the viscosity will not help overcome the yield value barrier because of these terms. not in the shear equation. Increasing surface tension and coating thickness is optional, but has practical limits.
Yield value is usually controlled by shear (thixotropy), coating application rate and mixing— conditions can be important. High roller speeds (for roller coaters) and higher spray pressures (for spray guns) can temporarily give up yield. Clearly, good leveling is not achieved by the lowest surface tension. While good wetting may require lower surface tension, higher surfaces. Tension boosts levels. This is another reason to use the lowest effective level of surfactant.
