Ostwald CW. Ostwald, German chemist who won the Nobel Prize), created the Ostwald color system. Its hue circle is composed of 24 colors. Based on E. Hering's four-color theory, he separates orange, purple, blue-green, and yellow-green from the four colors of yellow, red, blue, and green. 8 basic colors. Then divide each color into 3 types to form 24 basic hues, which are represented by symbols respectively (see Table 8-1).
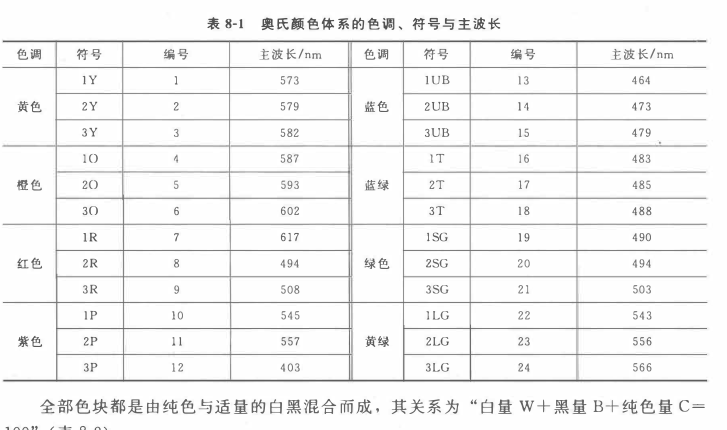
All color blocks are made of pure color mixed with appropriate amount of white and black, and the relationship is "White Amount W + Black Amount B + Pure Color Amount C = 100" (Table 8-2).

The Austenitic color solid is composed of a complex cone, and the north and south poles of the vertical central axis are black (B) and white (W)' respectively. The 8 symbols on the axis a, C, e, g, l, l, n, p, are respectively Neutral gray with gradual lightness; the longitudinal section is diamond-shaped, and the central axis divides the rhombus into two symmetrical color triangles that are complementary colors; the color triangle is divided into 28 small rhombuses, respectively composed of ca, ea, ga, 1a, la , na , pa , ec , gc , IC, le, nc , pc , ge , ie , le , ne , pe , 1g , lg , ng , pg , h, m, pi , nl , pl , pn28 symbols represent , the first letter represents the white content in the color scale, the second letter represents the black content in the color scale, and the vertex of the color triangle is a pure color, represented by the symbol C. For example, if the color standard of a certain pure color is nc, n is the white content of 5.6%, and C is the black content of 44%, then the pure color contained in it is: 100- (5.6 + 44) = 50.4 (% ), and another example is that the solid color standard is pa, p contains 3.5% mortar, and a contains 11% black. So the pure color content is: 100 — (3.5+11)=85.5 (%).
In the Austenitic color triangle, the side perpendicular to the central axis is the lightness series, the upper side is the light color series, and the lower side is the dark color series inner triangle surrounded by three sides is the turbid color series with gray; the color series parallel to the central axis The groups are equal purity series, the color groups parallel to the upper line are equal black volume series, and the color groups parallel to the lower line are equal white volume series. The determination of each color scale is based on the ratio of pure color, white content, and black content contained in the color on the swivel board through rapid rotation space mixing and reproduction (Figure 8-9 Ostwald color triangle).
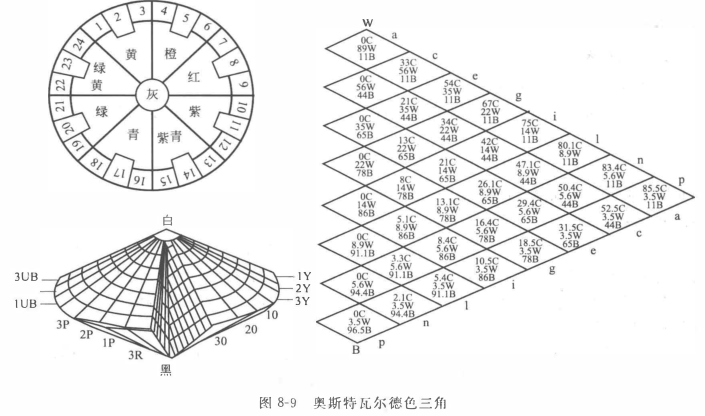
Each color scale in the Austenitic color system is represented by hue number/white content/black content, such as 8 ga: No. 8 color is red This color is light red with high brightness. The Austenitic color system is easy to understand, and it provides useful instructions for those who use colors. When doing the transition of purity in the color composition exercise, the hue triangle can be regarded as a guide to the formula. In addition, the unity of the hue triangle also shows clear regular changes for the color matching characteristics.
The defect of this color system is that the establishment of equal hue triangles limits the number of colors, and if a new, more saturated color is found , it will be difficult to show it on the graph. In addition, the colors on the isohue triangle are all mixed colors of a certain saturated color and black and white, and the chromaticity coordinates of black and white should be unchanged in theory. The colors on the same isohue triangle all have the same dominant wavelength, but only different saturations, which is inconsistent with psychological colors. At present, color mixing discs are used to prepare triangles of the same hue to make up for this defect.
