Coating Thickness Gauges using ultrasonic measurement technology are becoming more and more popular. They support or replace destructive methods of measuring coating thickness on wood and wood products.
Coatings serve multiple functions. Some are used to restore, protect, waterproof and beautify wooden structures. Others are specially formulated to seal and fill pores and provide a nice surface texture. The permeable finish is absorbed into the wood and hardens to form a strong protective barrier that won't strip
Why measure thickness?
Coatings are designed to perform their intended function better when used within the thickness range specified by the manufacturer. For example, conversion varnishes should be used less than 5ml dry thickness than other paints to prevent cracking or other finish failures. Nitrocellulose lacquer should usually be kept lower than 3 mils. A consistent MIL thickness is important to apply the base coat and crack coat to achieve the desired crack finish.
On medium density fiberboard (MDF), the thickness of the powder coating usually ranges from 3 to 9 ml. Usually the thicker the thickness, the more durable the finish. Factory specifications usually call for a stated tolerance of 1 mil. This level of quality cannot be decided just by looking at it.
Accurately measuring finish has other benefits as well. When companies fail to inspect and verify the quality of incoming materials, they waste reworked product. Make sure the coating meets the manufacturer's recommendations by checking spray operator technique. Additionally, applying too much film thickness can greatly reduce overall efficiency. Finally, regular inspections can reduce the number of internal rework and customer returns due to processing defects.
How to test?
Testing coating thickness is commonplace for quality control and inspection purposes. When the base metal is carbon steel, the magnetic method is used. Eddy current devices are used on other metals such as copper and aluminum.
Since these instruments cannot measure the thickness of wood surfaces, alternative techniques were used:
Optical sectioning (cutting the coated part, viewing the cut) Height measurement (before and after measurement with a micrometer) Gravimetric (mass and area calculations for measuring coating thickness) Wet the Film Thickness Gauge into the wet paint and use the volume percent solids to calculate the dry film thickness Alternative (place a steel sheet over wood and paint at the same time).
Ultrasonic breakthrough
High-quality professionals are already familiar with all aspects of ultrasonic testing, in which high-frequency sound wave energy is used to perform inspections and measurements. Ultrasonic testing can detect and evaluate flaws in metals, measure dimensions, determine material properties and more.
Wall thickness measurement is perhaps the easiest and easiest method of ultrasonic testing. Precision ultrasonic wall Thickness Gauges allow rapid thickness measurement of objects without requiring two-way access. However, for coating measurements, these gages are not satisfactory. They do not have sufficient sensitivity to measure the thickness of acrylic filler plant primers, varnishes, UV topcoats, powder coatings and other materials used on wood.

Figure 1 PosiTector 200 Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge.
Acoustic Measurement Technology
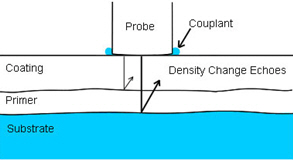
Figure 2 Ultrasonic waves return to the surface to be tested.
measurement accuracy
Placement of coating and substrate

图3不均匀的涂层/基体区两个例子。
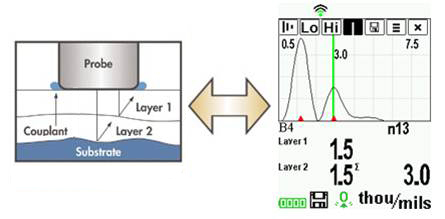
图4一些仪器测量多层系统中的各个层。在这个例子中,1层是1.5密耳厚。2层是1.5密耳厚,总厚度为3密耳。图形液晶displaystwo“峰”代表的是两材料界面。
确保正确的声音

图5无损检测木材漆层厚度.
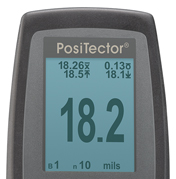
图6有些仪器提供统计分析。在这个例子中,10个被测量。18.2毫升的最后测量和显示的平均,标准偏差和所有10个读数的最大/最小值。

图7这些仪器操作简单,经济实惠和可靠的。
结束语
Reduce waste in coating by controlling the thickness of the coating being applied Reduce rework and repairs through direct feedback to operators and improve process control Objects that do not need to be destroyed or repaired to destroy coating thickness measurements