With the rapid development of CHINA's industrial economy, the application range of various harmful chemicals, flammable and explosive gases is constantly expanding. Leakage of these harmful, flammable and explosive gases during production and use will cause major accidents such as poisoning, fire and explosion. The gas alarm is a device that prevents the leakage of harmful, toxic, flammable, and explosive gases during production and use . In actual use, the alarm lower limit (such as 20%LEL, 10mol/mol) is set as the alarm point. Once a leak occurs, the gas concentration reaches the lower alarm limit (alarm point) and the alarm will immediately alarm and cut off the power supply . Turn on the ventilation system so that personnel can deal with the dangerous situation within a certain period of time.
The reliability of the alarm during use will be directly related to serious issues such as endangering people's lives, property safety and pollution of the natural environment. Therefore, it is very necessary to study the verification method of gas alarm to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the detection data and timely alarm.
Due to the wide variety of gases, the national measurement and verification regulations cannot cover everything. At present, the existing national measurement and verification regulations mainly include JJG693-2011 "Verification Regulations for Combustible Gas Detection and Alarms", JJG915-2008 " Verification Regulations for Carbon Monoxide Detection and Alarms", JJG695-2003 " Verification Regulations for Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Detectors" and other commonly used regulations. Analyze the verification regulations of combustible gas, carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide gas alarms. The verification of gas alarms is nothing more than the alarm setting value and alarm function , indication error, repeatability, response time, and drift of gas alarms. and other parameters to check.
Before the verification work starts, according to the working principle and performance characteristics of the gas alarm, connect the standard gas, the flow controller and the tested instrument as shown in the figure.
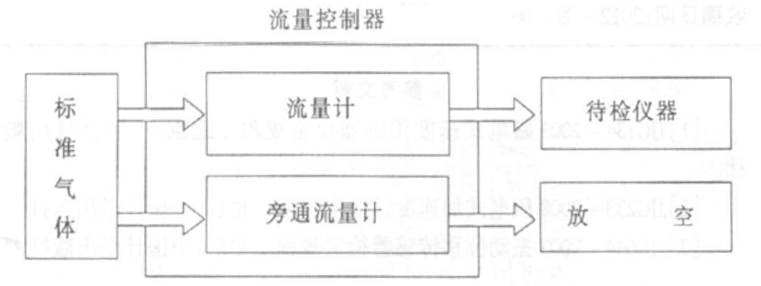
The specific methods in the verification process are as follows:
(1) The temperature of the verification environment should be kept at (0 ~ 40) ℃, and the relative humidity should be kept at ≤85%. At the same time, good ventilation is required, and there is no electromagnetic interference that affects the normal operation of the instrument.
(2) Before verifying the alarm, you need to get the alarm manual to understand the basic information such as the working principle and range of the instrument; secondly , make an accurate judgment on whether the alarm is working normally . The alarm does not respond . Check to see if the probe is blocked by debris (rust, dust, etc.), and if so, blow it off with compressed air ; Or the probe sensor is out of action.
(3) Selection of the standard gas flow rate: According to the different , use a flow controller to control the flow rate of the standard gas. When calibrating a diffusion instrument, the flow rate should be in accordance with the requirements of the instrument manual, and at the same time use the diffusion cover for calibration that is matched with the instrument. If there is no specific requirement in the instrument manual, it is generally controlled within the flow range of about 500mL/min; when verifying the suction instrument, its flow rate should be equal to the flow rate of the suction pump, and the bypass flow rate in the flow controller must also be ensured. The meter has flow to vent. Pay attention to the airtightness of the tube every time you use it, so as to prevent the false display of the value due to the leakage of the tube. For standard gases with different concentrations, the flow rate must be stable and uniform when verifying ventilation, so that the verified values can be accurate and reliable.
(4) Selection of pressure reducing valve and pipeline: According to the tested instrument and the standard gas used , use the pressure reducing valve ; pipeline materials that do not affect the gas concentration, such as combustible gas can If pipes made of materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene are used , for gases with high adsorption and corrosiveness such as chlorine gas and hydrogen sulfide, it is necessary to use pipes such as stainless steel that will not affect the normal verification.
(5) Verification of indication error: It should be verified after the instrument is powered on and preheated and stabilized . Because some sensors will stabilize after a certain period of warm-up after the power is turned on. During this period, the display value may fluctuate . This is just a transitional state, not a malfunction of the Detector, so ensure sufficient time for warm-up Stability is also an important measure to ensure the authenticity and reliability of the basic error ; at the same time, the full scale of the instrument should be calibrated first when verifying the indication error , which can achieve the purpose of saving standard gas.
(6) Verification of response time: Generally, the goal can be achieved . At the same time, it is necessary to emphasize the stability and uniform speed of the gas flow each time.
(7) Verification of alarm error: Each instrument has its corresponding alarm point, which has been set at the factory, so it should be calibrated according to the alarm , and the concentration of the input is about 1.5 The standard gas that is about times the set value of the instrument alarm (lower limit). The standard gas concentration should not be too small,
It can't be too large, otherwise it will not be conducive to the reading, or directly affect the reading.
(8) Repeatability verification: Since the repeatability is done after the verification of the indication error , the data of the indication error cannot be simply used, and it must be done again to obtain the value. Under normal working conditions, pass through the zero point gas to calibrate the zero point, and then pass through the standard gas for verification.
(9) Because the gas is flammable, harmful and poisonous, it will cause harm to the human body when the concentration reaches a certain range. For example, when the concentration of carbon monoxide reaches 1.6×10 -9 , it can cause headache and vomiting in 20 minutes, and cause death in 2 hours. Therefore , it is necessary to pay attention not only to the influence of residual gas on the test, but also to the influence of the exhaust gas on the human body during the test , and to increase the necessary equipment for ventilation and exhaust to ensure that the indoor air is clean.
references
[1] JJG695-2003 "Verification Regulations for Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Detector".
[2] JJG915-2008 "Verification Regulations for Carbon Monoxide Detection and Alarm".
[3] JJG693-2011 "Verification Regulations for Combustible Gas Detection and Alarm".












