Gas sensors are mainly used to detect a specific gas, and measure whether the gas exists near the sensor, or the content in the air near the sensor. Therefore, gas sensors are often important in safety systems. These sensors can provide security systems with information on combustible, combustible and toxic gases, as well as the consumption of oxygen and the proportion of carbon dioxide in the area.
Common gas sensors include electrochemical gas sensors, catalytic combustion gas sensors, semiconductor gas sensors, infrared gas sensors, etc. Due to different principles and structures, different types of sensors have different performances, usage methods, applicable gases, and applicable occasions. Today, I will list the common types of gas sensors for you, hoping to help you.
Electrochemical Gas Sensors
A considerable part of flammable, toxic and harmful gases, such as hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, etc., are electrochemically active and can be electrochemically oxidized or reduced. Using these reactions, gas components can be distinguished and gas concentrations can be detected. Electrochemical sensors are based on this principle.

Electrochemical sensors have many subclasses:
Primary battery type gas sensor
This sensor is also known as a Gavoni cell-type gas sensor, or a fuel cell-type gas sensor, or a self-generating cell-type gas sensor. Their principle is the same as the dry batteries we use every day, except that the carbon-manganese electrodes of the battery are replaced by gas electrodes. In the case of an oxygen sensor, the oxygen cathode is reduced and the electronic ammeter flows to the anode where the lead metal is oxidized. Therefore, the magnitude of the current is directly related to the oxygen concentration. This sensor can effectively detect gases such as oxygen, sulfur dioxide, and chlorine.
Constant Potential Electrolytic Cell Type Gas Sensor
This sensor is very effective for detecting reducing gases. Its principle is different from that of the original battery sensor. The electrochemical reaction occurs under the force of the current. It is a real Coulomb analysis sensor. This sensor has been successfully used in the detection of carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen, ammonia, hydrazine and other gases, and is currently the mainstream sensor for toxic and harmful gas detection.
Note: Coulomb analysis refers to the method of determining the content of the substance to be measured by Faraday's law according to the electricity consumed in the electrolysis process.
Concentration battery type gas sensor
The electrochemically active gas of this kind of sensor will spontaneously form a concentration electromotive force on both sides of the electrochemical cell, and the magnitude of the electromotive force is related to the concentration of the gas. The successful examples of this kind of sensor are oxygen sensors for automobiles and solid electrolyte carbon dioxide detection. instrument.
Limiting current type gas sensor
This is a sensor for measuring oxygen concentration. The working principle is based on the oxygen pump action of a stable zinc oxide solid electrolyte, and the limiting current is obtained by controlling the oxygen supplied to the cathode through gas diffusion. This sensor is currently mainly used for combustion control of boilers, detection of oxygen concentration in molten steel, and oxygen detection of automobiles.
Semiconductor gas sensor
The semiconductor gas sensor uses the oxidation and reduction reaction of the gas on the surface of the semiconductor, resulting in a change in the resistance of the sensitive element:
Oxygen and other gases with a tendency to adsorb negative ions are called oxidizing gases—electron-accepting gases;
Gases that tend to adsorb positive ions, such as hydrogen, hydrocarbons, and alcohols, are called reducing gases—electron-donating gases.

When the oxidation (reduction) type gas is adsorbed on the N (P) type semiconductor, the carrier of the semiconductor decreases (increases), and the resistivity increases (decreases); when it is adsorbed on the P (N) type semiconductor, the carrier of the semiconductor increases (decrease), the resistivity decreases (increases). (It can be seen that the oxidized and reduced semiconductors are diametrically opposite) Therefore, the corresponding gases can be effectively detected from these properties.
Semiconductor gas sensors can be effectively used for the detection of many gases such as methane, ethane, propane, butane, alcohol, formaldehyde, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, ethylene, acetylene, vinyl chloride, styrene, acrylic acid, etc. In particular, this sensor is low in cost and can meet the needs of both industry and civil use.
Disadvantages: poor stability, greatly affected by the environment, not suitable for applications where accurate measurement is required.
Catalytic combustion gas sensor
This sensor is actually a gas sensor based on a platinum resistance temperature sensor, that is, a high-temperature-resistant catalyst layer is prepared on the surface of the platinum resistance. Resistance changes.

Since the platinum resistance of the catalytic combustion gas sensor is usually surrounded by ceramic beads composed of porous ceramics, this sensor is usually also called a catalytic bead gas sensor. In theory this sensor can detect all combustible gases, but there are many exceptions in practical applications. This sensor can usually be used to detect combustible gases such as methane, LPG, acetone, etc. in the air.
Based on the excellent temperature characteristics of platinum resistance, this sensor has accurate measurement and fast response. The sensor output is directly related to the environmental explosion hazard, and the safety detection field is a kind of dominant position sensor.
The disadvantage is that it needs to work in an environment with sufficient oxygen (after all, it needs to burn); working with dark fire, there is a danger of ignition and explosion; most elemental organic vapors have a poisoning effect on the sensor; due to the continuous consumption of catalysts, the zero point and range will drift. Frequent calibration and adjustment are required.
Photoionization gas sensor
通常被称为PID,即Photoionization Detector的缩写(仪控君在此特别提示,此PID不是比例微分积分)。这是一种具有极高灵敏度,用途广泛的检测器,可以检测从10ppb到较高浓度的10000ppm的挥发性有机物和其他有毒气体。许多有害物质都含有挥发性有机化合物,PID对挥发性有机化合物灵敏度很高。

PID使用了一个紫外光源,通过离子化,即将有机物分子电离成可被检测器检测到的正负离子,检测器捕捉到离子化了的气体的正负电荷,并将其转化为电流信号实现气体浓度的测量。当被测气体吸收高能量的紫外光时,气体分子受紫外光的激发暂时失去电子成为带正电荷的离子,气体离子在检测器的电极上被测出,According to电极产生的电位检测出气体浓度,检测后,离子很快又与电子结合重新组成原来的气体分子。
PID可检测芳香烃类、酮类、醛类、氯代烃类、胺及胺类化合物和不饱和烃类。
红外气体传感器
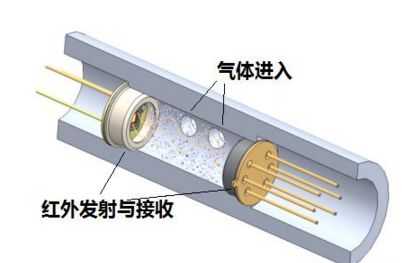
这种传感器利用气体对特定频率的红外光谱的吸收作用制成。红外光从发射端射向接收端,当有气体时,对红外光产生吸收,接收到的红外光就会减少,从而检测出气体含量。目前较专业的红外式采用双波长、双接收器,使检测更准确、可靠。
它的优点是:选择性好,只检测特定波长的气体,可以According to气体定制;采用光学检测方式,不易受有害气体的影响而中毒、老化;响应速度快、稳定性好;利用物理特性,没有化学反应,防爆性好;信噪比高,抗干扰能力强;使用寿命长;测量精度高。
缺点是:测量范围窄,只能检测(c1。c5)的碳氢化合物;怕灰尘、潮湿,现场环境要好,需要定期对反射镜面上的灰尘进行清洁维护;现场有气流时无法检测;价格较高。
固体电解质气体传感器

固体电解质气体传感器是指以固体电解质作为传感材料的气体传感器,常用的固体电解质主要包括:稳定氧化锆、钠离子快导体、质子导体以及一些低价金属的卤化物等。固体电解质气体传感器按照检测信号的特点可分为平衡电位型、混成电位型、限制电流型和短路电流型等。
This sensor is between the semiconductor gas sensor and the electrochemical gas sensor, and its selectivity and sensitivity are higher than that of the semiconductor gas sensor, and its life is longer than that of the electrochemical gas sensor, so it is widely used. The disadvantage of this sensor is the long response time.
Ultrasonic Gas Detector

This kind of Gas Detector is quite special. Its principle is that when the gas leaks from the high-pressure end to the low-pressure end through a small leak hole, turbulent flow will be formed and vibration will be generated. Typical turbulent airflow will become a factor when the differential pressure is higher than 0.2MPa, and ultrasonic waves will be generated if the pressure exceeds 0.2MPa. Turbulent molecules collide with each other generating heat and vibrations. Thermal energy is dispersed quickly, but vibrations are transmitted over considerable distances. Ultrasonic Detectors judge whether there is an air leak by receiving ultrasonic waves.
Such Detectors are typically found on oil and gas platforms, power plant gas turbines, compressors, and other outdoor pipelines.
Magnetic oxygen analyzer

This Gas Analyzer is based on the physical phenomenon that the magnetic susceptibility of oxygen is much greater than the magnetic susceptibility of other gases, and it is a physical gas analysis equipment that measures the oxygen in the mixed gas. This device is suitable for automatic detection of oxygen content in various industrial gases. Such devices can only be used for oxygen detection and have excellent selectivity.









