From the experimental discussion and analysis, it is known that according to the volume solid content of industrial paint, the theoretical brushing area of the paint at different dry film thicknesses can be calculated, and then the theoretical dosage of engineering paint can be withdrawn. In this paper, the calculation method of the volume solid content of industrial paint is obtained from the three parts of calculation method definition, formula derivation, and example verification. This calculation method has a very important guiding role in formula design and coating construction application.
For a long time, people have analyzed and discussed the mechanism and law of metal corrosion, and applied different technologies to maintain metals. Avoiding corrosion and prolonging the service life of metal materials has always been a worldwide research topic [1]. So far, painting anti-corrosion coatings on metal surfaces is a widely recognized method that can prolong the service life of metal materials. The type of coating, supporting technology and construction quality all have a great influence on the quality of anticorrosion. With the continuous development of industrial paint, the coating industry also tends to be specialized. The volume solid content mainly discussed in this paper is a very important issue in the coating industry, which refers to the ratio of dry film volume to wet film volume[2]. According to the volume solid content, people can calculate the theoretical painting area of the paint under different dry film thickness before painting, that is, volume solid content × 10 ÷ thickness = theoretical painting area (m 2 /L), and then calculate the coating area of the project Theoretical dosage. It can be seen that the volume solid content has a very important influence in industrial coatings and their coating industry.
Calculation method of volume solid content
1. Definition
According to the definition, the volume solid content V% = (V 1 /V 2 ) × 100%. Among them, V% ─ solid volume solid content (hereinafter referred to as volume solid content), V 1 ─ dry film volume, V 2 ─ wet film volume. For a cuboid membrane, volume = base area × thickness, so V% = (V 1 /V 2 ) × 100% = [(A ×δ 1 )/(A × δ 2 )] × 100% = ( δ 1 /δ 2 ) × 100%. Among them, δ 1 ─ dry film thickness, δ 2 ─ wet film thickness, A ─ steel plate surface area. Modern thickness measurement technology is relatively professional, and both dry film thickness and wet film thickness can be well measured by instruments. When measuring the thickness, it is advisable to use the spraying method to make the board, so that a uniform coating film can be obtained, which is beneficial to the measurement. After spraying, the detection of wet film thickness is affected by solvent volatilization, so wet film measurement should be completed within 5 minutes after construction to reduce errors; dry film thickness should be measured after the paint film is completely dry. Different types of coatings have different drying times, and the dry film thickness is usually measured after 24 hours of spraying, and the error is small. The definition method to measure the volume solid content is an intuitive and quick measurement method, but the disadvantage is that when measuring the dry and wet film thickness (measuring instrument: wet Film Thickness Gauge), it is necessary to obtain a large number of measured values, and then take the average value to reduce the Measurement error.
2. Inverse algorithm to measure volume
1. Formula derivation
Known from method 1,
V% = (V 1 /V 2 ) × 100% = (A × δ 1 ) / V 2 × 100% , namely
V%/δ 1 = (A/V 2 ) × 100% (1)
In formula (1), A/V 2 (the unit is m 2 /m 3 ) represents the paintable area per volume of paint. If the units of each physical quantity in formula (1) are expressed in common engineering units, then we can get
V% = (A/V 2 ) × δ 1 /1 000 (2)
Wherein, the unit of δ 1 is μm, and the unit of A/V 2 is m 2 /L (that is, the theoretical painted area familiar to engineering applications, TSR). Therefore, as long as the TSR of the corresponding thickness is calculated, the volume solid content of the coating can be obtained.
2. Determination of theoretical coating area (TSR) of paint
First weigh the mass (M 1 ) of the steel plate with a known area (A) on a balance with a sensitivity of 0.01 g [3], then spray the paint evenly and make the plate, and immediately weigh the mass of the steel plate after spraying (M 2 ) , then the theoretical coating area TSR = A/(M 2 − M 1 ). Since the standard unit is m 2 /kg, it is necessary to measure the wet film density ρ 2 (kg /L, the same below) of the coating.
Since m 2 /kg × kg/L = m 2 /L, so
A/V 2 = A/(M 2 − M 1 ) × ρ 2 .
Substituting the calculated TSR into formula (2) (the corresponding thickness has been measured), the volume solid content of the coating can be calculated. It is worth noting that when the board is made by spraying, the paint sometimes needs to be diluted during construction, so the amount of dilution needs to be considered in the calculation. Thin paint as above
If the release amount is Y, the amount of paint sprayed is not (M 2 − M 1 ), but (M 2 − M 1 ) × (1 − Y). Similar to method 1, the error of the inverse algorithm is mainly generated in the process of detecting the theoretical coating area TSR and measuring the thickness of the paint.
3. Volume addition method
According to the definition V% = (V 1 /V 2 ) × 100%, V 1 is regarded as the addition of the volumes of the solids. For the convenience of calculation, assume that the wet film mass of a coating is m 2 (the corresponding wet film density is ρ 2 , the same below), and the mass of each solid component is ma (the corresponding density is ρ a ), mb (the corresponding density is ρ a ) and mb (the corresponding density is ρ b ), mc (the corresponding density is ρ c )..., then
V 1 = ma /ρ a + mb /ρ b + mc /ρ c + …
V 2 = m 2 /ρ 2 , namely
V% = (V 1 /V 2 ) × 100%
= (ma /ρ a + mb /ρ b + mc /ρ c + …) × (ρ 2 /m 2 ) × 100%
When using the volume addition method to calculate the volume solid content, it should be noted that the dry volume of the resin (or emulsion) in the coating is obtained by dividing its solid content by its dry density.
For developers who are familiar with paint formulations, the volume addition method is a good theoretical calculation method. The main source of error in this method is that when calculating the solid volume, the dry film volume V 1 is simply regarded as the sum of the volumes of the individual solids. In fact, due to molecular gaps and other reasons, the actual dry film volume of each solid component will be slightly smaller than the sum of the volumes of each solid component after mixing.
4. Volatile volume solid content method
Let V(volatility)% be the ratio of the volume of volatile matter in the coating to the volume of the wet film (i.e. the volume solid content of volatile matter), then the volume solid content of non-volatile matter V% = 1 − V(volatility)%. Similar to the method in 2.3, V (volatility)% is equal to the sum of the volume content of each volatile in the coating, and the calculation method will not be discussed in detail. When the volatile component in the system is relatively single, or the density of each volatile component is close, the following method can be used to calculate V (volatility)%.
First, the mass solid content in the paint is measured m%, then the mass content of volatile matter is 1 − m%, and the density ρ of volatile matter can be taken as the average value of the density of each component, or directly take the density of the volatile matter with the largest content as The average density (for example, for water-based paint, the density of water can be directly taken as the average density), so it is not difficult to calculate V%.
V% = 1 − V(wave)%
= 1 − [m 2 (1 − m%)/ρ]/(m 2 /ρ 2 )
= 1 − (1 − m%)ρ 2 /ρ
In the above formula, m% ─ mass solid content, m 1 ─ mass of dry film, m 2 ─ mass of wet film, ρ 1 ─ density of dry film, ρ ─ average density of volatile matter, ρ 2 ─ density of wet film.
The error in the volume solid content method of volatiles is that the density of volatiles is not actually equal to the average value of each volatile density, but equal to the sum of the products of each volatile density and its content in volatiles. However, the above algorithm is very practical when the volatile component is relatively single or one of the volatile components accounts for a large proportion.
25. Measure volume solid content by density method
From V% = (V 1 /V 2 ) × 100%, get
V% = (m 1 /ρ 1 )/(m 2 /ρ 2 ) × 100%
= (m 1 / m 2 ) × (ρ 2 /ρ 1 )
= m% × (ρ 2 /ρ 1 )
The physical meaning represented by V% = m% × (ρ 2 /ρ 1 ) is that the solid volume solid content of the coating is equal to the mass solid content of the coating multiplied by the ratio of wet film density to dry film density.
In the above formula, both the mass solid content m% and the wet film density ρ 2 can be obtained through routine testing. For the dry film density ρ 1 , there are two calculation methods:
(1) According to the wet film volume is equal to the sum of dry film volume and volatile matter volume, m 2 /ρ 2 = m 1 /ρ 1 + (m 2 − m 1 )/ρ. Each variable can be obtained by calculation or detection, so it is not difficult to calculate the value of ρ 1 .
(2) According to Archimedes' law[4], hang the dry paint film on the balance hook with a thin steel wire, immerse the sample in water, weigh the mass in the water (accurate to mg), and then press the formula (paint Solid fraction density = mass of dry paint film in air ÷ (mass of dry film in air − mass weighed in water + mass of suspension wire). The physical meaning of this formula is to use the principle of mass/volume to obtain the desired result. However, it must be noted that when weighing in water, the air bubbles on the surface of the paint film and between the interlayers should be driven out, otherwise the measured density will be low.
In engineering applications, it is only necessary to measure the mass solid content in m% and the wet film density ρ 2 , and this method can be used to quickly calculate the volume solid content. Like the volatile volume solids method described in 2.4, the disadvantage of this method is that the density of the volatiles is not actually equal to the average of the individual volatile densities, but the product of each volatile density and its content in the volatiles Sum.
3. Example verification
The above calculation method can be used to verify its feasibility. If there is a water-based latex type anticorrosive paint, its parameters are shown in Table 1.
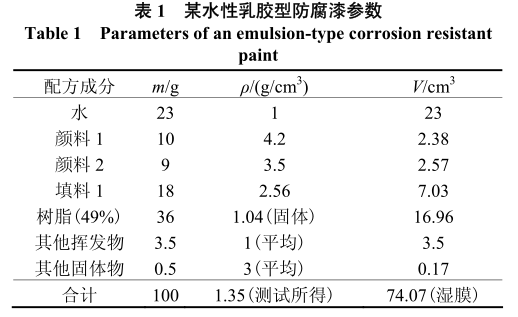
Use the above-mentioned different methods to calculate its volume solid content respectively:
(1) According to 2.1 method. Through multi-point testing of dry and wet film instruments
Average value, δ 1 = 35 μm, δ 2 = 89 μm, then
V% = (δ 1 /δ 2 ) × 100% = 35/89 × 100% = 39.33%
(2) According to 2.2 method. The known mass painted area is 8.31 m 2 /kg,
Its volume painted area is 8.31 × 1.35 = 11.22 (m 2 /L), then
V% = (A/V 2 ) × δ 1 /1 000
= 11.22 × 35/1 000
= 39.27%
(3) According to 2.3 方法。V 1 为表 1 各固体分体积的和,即 V 1 = 2.38 + 2.57 + 7.03 + 16.96 + 0.17 = 29.11 (cm 3 ),V 2 为湿膜质量(100 g,见表 1)与湿膜密度(1.35 g/cm 3 ,见表 1)之比,即
V 2 = 100/1.35 = 74.07 (cm 3 )
V% = (V 1 /V 2 ) × 100% = 29.11/74.07 × 100%
= 39.30%
(4) 由表 1 可知,挥发物的体积[V(挥)]由水、树脂挥发物和其他挥发物体积相加所得。其中,树脂中的挥发物是水,故树脂挥发物的体积是36 × 51% ÷ 1,则
V(挥)% = V(挥)/V 2 × 100%
= (23 + 36 × 51% ÷ 1 + 3.5) ÷ 74.07 × 100%
= 60.56%
V% = 1 − V(挥)%
= 1 − 60.56%
= 39.44%
或由表 1 算出质量固含量:
m 1 = 10 + 9 + 18 + 36 × 49% + 0.5
= 55.14 (g)
即 m% = 55.14%,则
V(挥)= (100 − 55.14)/1
= 44.86 (cm 3 )
V% = [1 − V(挥)] × 100%
= [1 − 44.86/74.07] × 100%
= 39.44%
(5) According to 2.5 方法。质量固含 m% = 55.14%,则
ρ 1 = m 1 /V 1
= 55.14/(74.07 − 44.86)
= 1.89 (g/cm 3 )
V% = m% × (ρ 2 /ρ 1 )
= 55.14% × 1.35 ÷ 1.89
= 39.38%
4 总结
从实验结果表明:体积相加法、挥发物体积固含量法、密度法与公式推导都较为接近,可确定此理论计算办法可行应用。并且对该涂料体积固含量进行判定,即该涂料体积固含量在 39% ~ 40%之间。
5 Research Outlook
During routine construction operations, the construction party will roughly estimate the amount of paint used based on the volume solid content given by the paint manufacturer, so that the cost performance of the paint can be compared. The author has many years of construction experience and understands that many paint manufacturers often give a relatively large volume solid content in order to obtain a strong competitive advantage of the paint, which will mislead the buyer.
In this paper, through the volume addition method, the volatile volume solid content method, and the density method, the operator only needs to measure the mass solid content and wet film density of the sample paint to obtain the volume solid content. For the formulator, how to increase the volume solid content of the coating is also a very important environment in the process experiment.
For more details, please refer to Chen Haihong's "Discussion on the Calculation Method of Volume Solid Content of Industrial Paints"
