Two methods of preservation are better than one. This is the theory behind the dual protection coating system, which combines the proven protection of galvanizing with the advantages of an additional anti-corrosion system such as polymer powder coating. Using two coats, one on top of the other, increases the substrate's resistance to attack by corrosive substances in the working environment and extends the productive life of the asset. In some cases, duplex systems can also extend maintenance intervals, improving project lifecycle ROI.

How Duplex Systems Provide Additional Protection
While the zinc-iron alloy produced in the galvanized coating acts as a primer and becomes an impermeable barrier to the steel substrate, when special polymer coatings are added, corrosion protection can be extended up to 1.5 of the total arithmetic life times up to 2.5 times for two separate systems. In other words, if you have a polymer coating system that lasts 10 years and a hot dip galvanized system that is expected to last 50 years, for a total of 60 years (50 years + 10 years), the duplex system will actually last 90 years - 150 years. That is, if you allow both coats to wear away completely.
The demand for dual-phase coated steel occurs in the following areas:
Specialty Cladding Materials for Residential, Commercial and Industrial Needs
building products
Construction and Building Products
car
aviation
appliance
Chemical
oil
Advantages of double-sided coating
The double-sided coating system has the following advantages:
Extended and enhanced corrosion protection. No other protection system can match this enhanced protection alone.
Coated galvanized steel can provide an attractive aesthetic appearance, allowing the brightness and color of the steel to match specific locations and environments.
Maintenance costs are reduced as the duplex system significantly extends the production life of steel products. As a result, the total lifecycle costs are also reduced.
Steel can be painted to comply with safety color regulations.
After the top coat has worn away, zinc continues to provide corrosion protection until the structure is recoated on site. Weathered zinc alloy on the surface facilitates recoating with minimal cleaning.
Galvanizing and Metal Bonding
Galvanizing creates a metallic bond between the steel and the zinc, forming a barrier embedded in the structure of the base metal. In this metallurgical process, the zinc reacts with the molecules of the steel to form a series of zinc-iron alloy layers, as shown in this sketch:
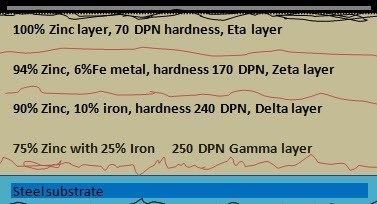
The microstructure of a galvanized coating consists of the following layers:
Inner alloy layer with 75% Zinc and 25% Iron (Gamma) Hardness 244 DPN
A layer of 90% zinc and 10% iron metal (Delta)
A layer of 94% Zinc and 6% Iron (Zeta)
The outer layer is 100% zinc with a hardness of 70 DPN
(Diamond Pyramid Number (DPN) is a measure of the indicative hardness of a layer.)
坚硬的Gamma,Delta和Zeta层通过磨损提供强大的机械损伤保护,而顶部的韧性Eta层为涂层提供抗冲击负载。甲镀锌层是因为与铁锌的合金化的尤其粘附到铁和钢。这种硬度和延展性的结合为锌涂层提供了很好的优势。(您可以在文章镀锌及其在防腐方面的功效中了解更多有关镀锌的好处。)
准备用于聚合物涂层的镀锌钢
在镀锌钢板上涂覆聚合物涂层类似于钢的涂漆工艺,没有任何先前的涂层。当然,在某些情况下,表面处理可能显着不同,这取决于电镀后经过的时间。ASTM D6386标准提供了表面处理的详细程序。
创建有效的双面涂层涉及以下步骤:
与客户和其他人沟通
评估和确定镀锌表面的状况
确保有效清洁表面
形成表面轮廓
涂上涂层并完全固化涂层
与客户和其他人沟通
正如质量管理体系(如ISO 9001)中通常所规定的那样,对客户要求的全面审查和澄清,以及镀锌机,制造商,涂料供应商,油漆工和腐蚀工程师等其他方的要求和期望是非常重要的。确保有效和有效的双面涂层。有关各方可能需要特定的处理,存储和处理特定参数,这些参数可能会影响完成任务所采用的设计或程序。
评估锌涂层的状况
当镀锌钢暴露于室内或室外环境时,由于风化而形成副产物。According to是新表面,部分风化表面还是完全风化表面,清洁和分析需要采取不同的操作。
还有一些镀锌表面缺陷可以通过镀锌机修复。该浮渣和略读夹杂物以及其他类似的缺陷需要被删除。如果电镀器被告知双面涂层,他或她可以确保消除任何此类缺陷。
新鲜锌涂层(镀锌后48小时内)镀锌后48小时
内,锌涂层会发出明亮的光泽或暗淡的颜色,只需要进行温和的清洁和仿形,以确保聚合物涂层的附着力。
部分风化(镀锌后一年内)
部分风化的锌涂层会显示一些锌化合物以及一些污染物,如油,污垢,灰尘或油脂。一些锌化合物可能粘在锌涂层上,需要通过研磨,仿形和清洁除去,以确保聚合物涂层的粘附。清洁过程需要确保原始锌层不会丢失。
完全风化(镀锌后两年以上)
如果镀锌钢表面完全被碳酸锌和其他化合物覆盖,则碳酸锌强烈粘附在表面上,不溶于水。因此,不应该删除它。在这种情况下,只需要清洁。
表面清洁
方法如下:
如果是部分风化或新镀锌的表面,请刮去去除凸起和滴水。
去除油性有机污染物,除了新镀锌表面。
在所有这三种情况下,用水冲洗镀锌金属,清洁干燥。使用手动研磨机去除新镀锌表面上多余的锌(如果有的话)。
在碱性溶液中清洁
使用10%碱性溶液从表面除去油性和有机污染物,对锌涂层的损害最小。如果溶液用于压力喷雾清洗,则不应使用高压(最大1400 psi)。(有关此主题的更多信息,请参阅爆炸压力:如何正确使用。)
酸洗有时使用
4%酸洗两分钟以去除有机污染物。通过刷子进行清洁,并在酸洗后进行两次漂洗。
溶剂清洗
溶剂使用干净的布料去除某些类型的污垢。在水漂洗之后,将镀锌钢部件干燥并送至成型部分。
表面轮廓
一旦清洁过程完成,就对表面进行成型(粗糙化),以便为涂层提供抓握(咬合)。用于表面轮廓分析的方法是:
表面扫掠爆破
洗底漆
表面采用丙烯酸处理
研磨处理
表面扫掠爆破通过使用低于60度角的温和磨料进行表面扫掠爆破。仔细选择研磨材料以避免损坏软顶锌涂层。
洗涤底漆
洗涤底漆过程基于其酸组分。该组分与锌表面反应,从而形成薄膜,其粘附在锌和随后的聚合物涂层上。
丙烯酸类治疗
的酸性元素丙烯酸治疗粗糙化锌涂层,并创建一个丙烯酸层,以允许随后的涂层粘附性。
研磨处理
在某些情况下,在新的热浸镀锌表面的情况下,可能需要进行表面研磨以改善顶部轮廓。研磨机可用于粗糙化顶部表面以获得适于聚合物涂层粘合的表面。除锌应限制在1 mil以内。
涂料或涂料应用
与在工厂涂覆的方法相比,用于涂覆和涂料应用的程序和方法在现场应用中变化很大。在现场应用的情况下,需要始终牢记天气状况,安全和健康方面。
现场涂层
镀锌钢部件清洁和成型后,应尽快进行涂层。涂覆或涂漆可以通过喷涂或刷涂在异形表面上来完成。涂层表面涂层/涂料配方的相容性需要由涂层供应商确认。
ASTM B201,可以测试镀锌表面由于淬火而存在于表面上的任何钝化剂。(在淬火如何改善金属性能的文章中检查淬火。)涂料配方需要与所用的钝化剂相容。
烘烤
在镀锌表面经过适当清洁和成型后,零件已准备好烘烤。被涂在锌涂层中的水或空气会导致涂层中出现针孔或气泡,除非在涂层施工前对部件进行加热或烘烤。在烘烤之后,可能需要稍微冷却部件以允许涂覆施加。
涂料和固化
粉末通常喷涂在镀锌表面上。在液体涂层的情况下,可以通过刷涂或喷涂来施加。在施加底漆之后,在施加面漆之前,涂层将需要热固化和淬火。最初,可以涂覆样品,并且可以检查程序的有效性作为预防措施。在顶部涂层完成后,可以再次完成固化和淬火。可以在每个阶段检查涂层以确定其有效性。
工厂环境中双面涂层的阶段
工厂遵循的程序将与现场程序不同。在自动化钢厂和批量生产厂之间,方法可能有很大差异。在大多数情况下,新镀锌钢在工厂涂漆或涂层。以下阶段通常适用于计算机控制的钢铁厂。
准备阶段
第一阶段是准备用于涂层的基材。首先在碱性溶液中,化学浴中清洗。清洗槽配有流体泵,输出到喷嘴,刷辊带有柔软的尼龙刷毛,用于机械刷洗。罐的碱性流体浓度可以According to镀锌表面上的油,油脂和其他污染物的程度而变化。浴的浓度是关键的质量参数。
接下来,基板通过冲洗槽,然后准备转换涂层以制备表面轮廓。它通过含有转化涂层的罐。或者,使用涂布机将转化涂层施加到基材条带的两侧。接下来,条带移动到干燥炉以消除转化涂层中的水分。
底漆涂层
干燥的带材通过底漆涂布机,其中通过涂胶辊涂布底漆涂层,例如环氧树脂。通常保持3至5微米的涂层厚度。固化在百年烤箱中完成。仔细控制时间和烘箱温度,以便很好的地固化涂层和涂层材料的厚度。在线圈到达顶部涂层部分之前,它是水淬的。
顶部涂层通常在最终涂层部分中实现最终的聚合物顶层,例如15-20微米的聚酯或聚乙烯二氟化钨(PVDF)。其他使用的涂料是丙烯酸树脂,PVSF,增塑溶胶,乙烯基树脂和醇酸树脂。通过改变涂层物质的浓度,线圈张力和系统速度来实现规定的顶部涂层厚度。最后的固化在随后的百年烤箱中完成,其中烤箱温度和线圈的速度仔细匹配。
最后将涂覆的线圈淬火并According to客户要求切割成一定尺寸。测试样品的耐腐蚀性。
Factors Affecting Lifetime of Duplex Coatings
In the case of automatic coating lines, tension adjustment and speed determine the quality of the coating. Other important parameters are:
Alkaline Cleaner Concentration
Bath concentration for conversion coating
Curing (baking) time in oven
Uniform temperature and good cure time in primer and topcoat ovens
Final test of double-sided coating
Final tests for double-sided coatings include:
Test resistance to mechanical damage (shock test)
The test is performed in accordance with ASTM 2774-84: Impact Test Method. This method examines the tendency of coatings to crack and lose adhesion under impact loads.
adhesiveness
The Bend Test In the bend test, the samples were tested according to ASTM D4145-83 using a bending machine. Any delamination, peeling or cracking will be considered a sign of failure. Test after primer coat to determine if the concentration of the conversion coating bath and the concentration of the primer coating bath are adequate.
Flexibility and Crack Resistance
Test This test determines the resistance of the coating to cracking when subjected to a 180 degree bend. It is done by using a tapered mandrel. The procedure followed was according to ASTM D522.
Coating hardness test
The sensitivity to mechanical damage during handling was evaluated by the pencil test (hardness test). Follow ASTM D3363-74 procedure.
chemical resistance
This test is very important when exposed to acids, alkalis and their compounds. Individual samples were immersed in 5% alkali (Noah) and 5% acid (H2SO4) solutions for one day, respectively. Note color change, blistering, cracking, dissolution and loss of luster.
Salt spray assessment
This procedure is listed in ASTM B11. This test is used to predict a coating's ability to protect steel in an atmosphere containing salt and moisture. Salt spray was prepared from a 5% sodium chloride saline solution. Corrosion detected after regular intervals is recorded. If the sample does not corrode, it indicates a coating suitable for marine environments.
heat resistance
This test indicates the ability of the coating to perform under high temperature conditions. A muffle furnace was used for this test. Blistering, tarnish and color change were observed after hourly heat exposure.
Methyl ketene test
This test follows ASTM 4752 and is an indicator of the coating's propensity to peel off under the influence of the chemical solvent methyl ketene. With the help of cotton wool, MEK was rubbed 100 times over the coating. Carefully note and record any peeling of the coating. It is an indicator of the solvent resistance of the coating.









