Paints are used to decorate, protect and extend the life of natural and synthetic materials and as a barrier against environmental conditions.
Coatings can be broadly divided into decorative coatings, which are applied on site to decorate and protect buildings and other objects, and industrial coatings, which are applied in factories to finish manufactured goods such as automobiles.
composition of paint
Paint contains:
Pigments - Primary pigments that impart color and opacity
Binder (resin) - a polymer, often called a resin, that forms a matrix to hold pigments in place
Extenders - add larger pigment particles to improve adhesion, strengthen films and save binders
Solvents (sometimes called thinners) - use organic solvents or water to reduce the viscosity of paint for better application. Water-based paints are replacing some paints that use volatile organic compounds, such as hydrocarbons that are harmful to the atmosphere.
Additives - used to alter the properties of a liquid paint or dry film
The binder (resin) and solvent together are sometimes called a vehicle. The binder can be dissolved as a solution or carried as a dispersion of microscopically small particles in a liquid.
Depending on coating type and application, additives may include:
Dispersant - separates and stabilizes pigment particles
Silicone - improves weatherability
Thixotropic agent - gives the paint a jelly-like consistency that breaks down into a liquid when stirred or brushed into it
Desiccant - speeds up drying time
Anti-settling agent - prevents pigment from settling
Bactericides - save waterborne paint in tanks
Fungicides and Algaecides - protect exterior paint films from mold, algae and lichen damage
Coatings are formulated according to their proposed use - primer, base coat, special coating (matt, gloss, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance). The pigment powder is broken down into individual particles which are coated and dispersed in a binder (resin) - this is called "wetting". Solvent is then added to give the desired consistency. Mix each batch of ingredients thoroughly in a large mixing vessel with desired additives (Figure 1). Coatings up to 40 000 dm3 can be prepared in one batch.
| Figure 1 Contents of white gloss (alkyd) paint and white matte emulsion (acrylic) paint. |
This unit discusses binders commonly used after pigments.
binder in paint
Three important binders (resins) used in modern paints are:
Acrylic polymer (resin)
Alkyd Polymers (Resins)
epoxy polymer (resin)
Acrylic polymer (resin)
The binders in many latex paints are based on homopolymers or copolymers of vinyl ethyl acetate (vinyl acetate) and acrylate (acrylic acid) esters.
Vinyl acetate is prepared by passing a mixture of acetic acid vapor, ethylene, and oxygen over heated palladium(II) and copper(II chloride):
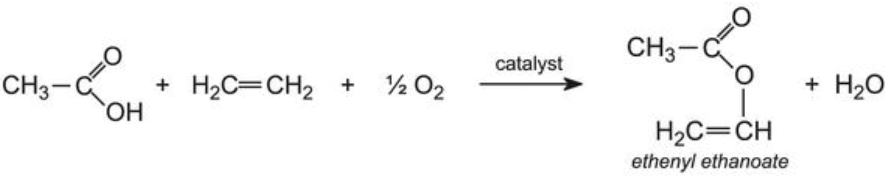
然后将乙酸乙烯酯和丙烯酸酯(例如,2-甲基丙烯酸甲酯)共聚以形成随机阵列,其中这些基团连接成直链:
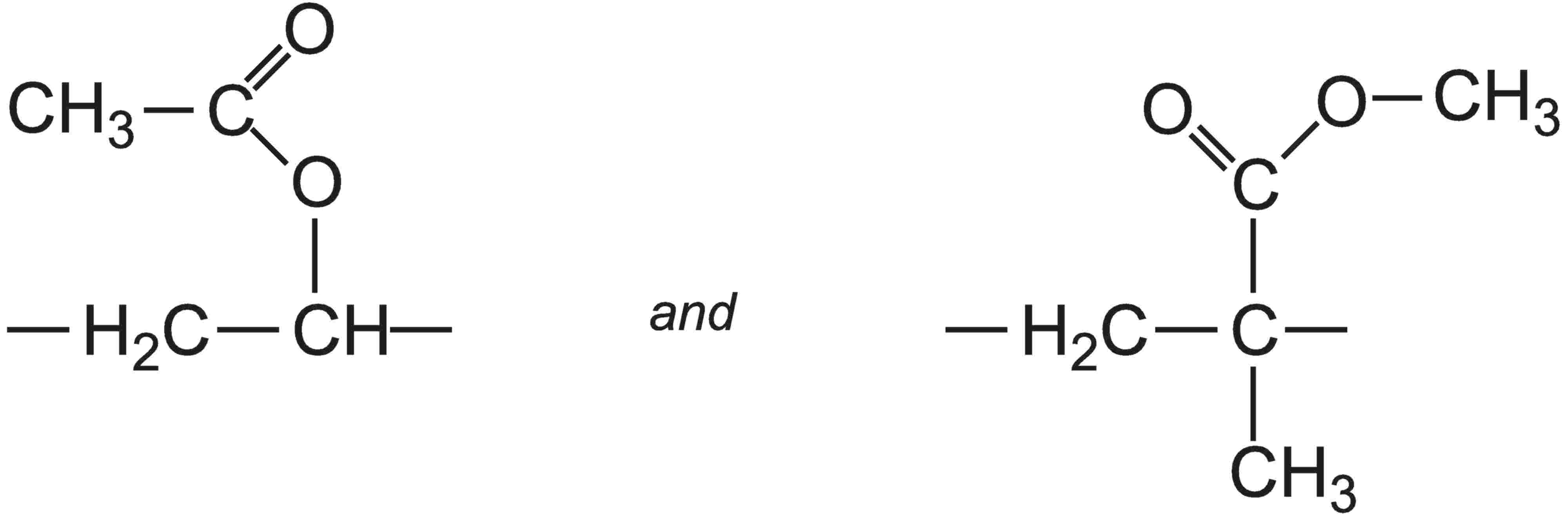
用作乙烯基乙酸乙酯的共聚单体的其它丙烯酸酯是丙烯酸乙酯,丙烯酸丁酯,或丙烯酸丁酯和2-甲基丙烯酸甲酯的共聚物。
这些涂料中使用的聚合物是在水中携带的(水性乳胶漆),如上所述,与粘合剂在有机溶剂中的涂料相比,它对环境要好得多。
| 图2水性乳胶漆用作装饰涂料,特别是建筑物内外(包括砖石涂料和外部底漆)。 得到阿克苏诺贝尔的亲切许可。 |
|
乳液涂料是所谓的乳液涂料,因为它们是通过称为乳液聚合的方法制备的,其中待聚合的液体单体首先作为乳液分散在水中。通过该方法生产的聚合物通常具有500,000-1,000,000的相对分子量。因此它们仅可用作分散体,因为如果它们在溶液中携带它们将是非常粘稠的并且这将使它们不可用。
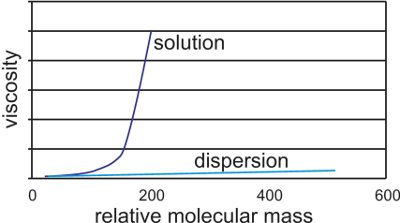
图3显示
溶液和分散聚合物的相对分子质量和粘度之间的关系的图。
丙烯酸树脂也可用于工业涂料中,作为水性乳胶漆或溶剂型涂料。溶剂型工业涂料可具有坚韧的保护性涂层,并广泛用于工业中作为面漆,例如在车身上。涂料经常作为两种组分在使用前混合在一起:主涂料部分通常由丙烯酸树脂组成,丙烯酸树脂是由多元醇(二醇和三醇)形成的丙烯酸酯的聚合反应制得的。所得聚酯具有许多从聚合物主链悬垂的羟基(-OH)。羟基与通常由聚合异氰酸酯组成的其他化合物反应,例如1,6-二异氰酸根合己烷(六亚甲基二异氰酸酯)的三聚体:
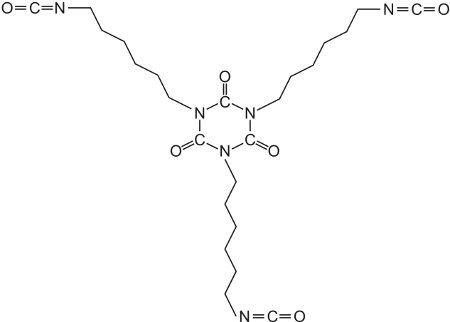
这种化合物被称为交联剂,它在与树脂反应时产生类似于由多元醇和异氰酸酯形成的聚氨酯的三维结构。
当这两种组分混合在一起时,聚合物(丙烯酸树脂)上的羟基与交联剂上的异氰酸酯基团之间发生化学反应:
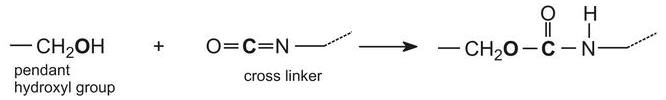
该反应在室温下相对缓慢地进行,允许涂料有足够的时间,然后溶剂稀释剂蒸发,并将涂漆的物品放入烘箱中以加速化学反应。这大大增加了聚合物的分子量,使其成为三维分子并形成耐化学品的硬膜。
醇酸聚合物(树脂)
装饰性光泽涂料通常含有醇酸树脂聚合物(树脂)。典型的树脂是由多元醇如丙烷-1,2,3-三醇(甘油)与二元酸如苯-1,2-二羧酸(邻苯二甲酸)酐和干性油(亚麻籽或大豆油)制成的树脂。 。在一起加热时,形成酯键,水是副产物。醇酸树脂的名称来源于醇和酸酐。
制备醇酸树脂聚合物的第一步是三醇和干性油之间的反应,产生甘油单酯。例如:
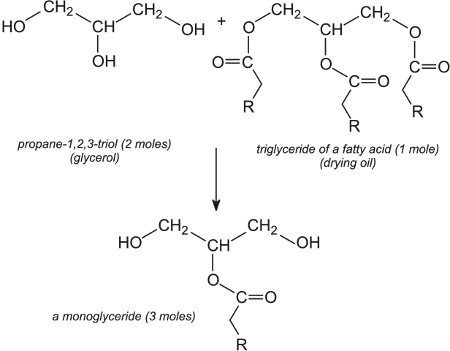
然后甘油单酯与酸酐反应形成醇酸树脂聚合物(树脂):

通常具有10 000-50 000的相对分子量的醇酸树脂通常在有机溶剂(溶剂型涂料)中携带。从树中提取的松节油过去曾用作溶剂,但这已经被来自石油化学原料的溶剂所取代,例如“白酒”,它是脂族和脂环族烃的混合物。
一旦涂覆醇酸树脂,悬垂的油干燥基团与空气中的氧反应,形成具有高分子量的交联的硬质热固性涂层。
环氧聚合物(树脂)
环氧树脂通常用作工业涂料(底漆)中的粘合剂。它们赋予涂料优异的附着力,同时具有高耐化学性(腐蚀性)和物理耐受性,例如在船舶和化学品储罐上。
环氧树脂由1-氯-2,3-环氧丙烷(由3-氯丙烯制备)和取代酚如双酚A制成:
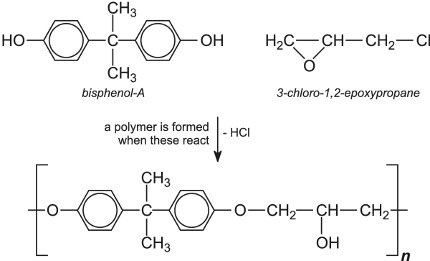
可以控制n的值以得到一系列树脂,从粘性液体到具有高熔点的固体。环氧树脂可以在溶剂中携带,例如芳烃,醇,酮和酯(溶剂型涂料)或作为真正乳液的水(水性涂料)中的分散体。它们通常不用于户外面漆,因为它们易受紫外线降解的影响,但它们可以制成很好的内部涂料和外部底漆。
环氧树脂也用作粘合剂(例如Araldite)和电绝缘体。
用于涂料的颜料
颜料赋予涂料颜色和不透明性。在有机颜料中,特别重要的是偶氮 -,酞菁和蒽醌衍生物。
常见的无机颜料是白色二氧化钛(氧化钛(IV)),其提供超过70%的所用颜料(单元51)。它具有高折射率并赋予涂料“光泽”。另一种广泛使用的无机颜料是细碎的碳酸钙。它具有低折射率,并与二氧化钛一起用于生产“哑光”涂料。其他颜料包括氧化铁(黑色,黄色和红色),氧化锌和炭黑。
粉末金属如锌和一些金属化合物,例如磷酸锌,具有腐蚀抑制性能。
油漆干燥
当涂料干燥时,形成薄膜,该薄膜粘附在其所施加的材料的表面上。
乳液涂料通过物理过程干燥,所述物理过程涉及水的蒸发,随后聚合物液滴的聚结以及随后整合到作为颜料的粘合剂的硬聚合物基质中。
在施加光泽涂料时,一旦溶剂大量蒸发,醇酸树脂聚合物通过与空气中的氧气的氧化反应交联。使用过渡金属盐(例如,环烷酸钴和锰)加速该反应。过渡金属离子(具有可变氧化态)催化聚合物链的交联,从而为涂料产生硬表面膜。
称心涂料的属性
这些According to特定的最终用途而变化很大。例如,汽车面漆的要求与装饰性天花板涂料的要求非常不同。
所需的一些典型属性可包括:
易于应用
良好的流动应用标记(例如刷痕)
形成连续的保护膜
高度不透明
快干
耐腐蚀性能
防水性
耐热性
颜色稳定性(即对抗可见光和紫外线辐射)
耐磨性和耐刮擦性
耐久力
灵活性
容易清理
| 图4这些是风化架。涂料已经应用于面板并且以与水平面和南面面成45°的角度暴露,以评估耐久性。受监测的特性包括:颜色变化(褪色),光泽变化,污垢吸收,开裂,剥落以及真菌和藻类污染。 经Q-Lab Europe Limited许可。 |
|
申请方法
使用了许多方法,包括:刷涂,辊涂,浸涂,流涂,喷涂,热喷涂,静电喷涂,无空气喷涂,电沉积,粉末涂覆,真空浸渍和浸渍。
环境问题
铅化合物不再用于装饰涂料和汽车涂料中。仍然在专业工业涂料中使用的铅化合物的数量已大大减少,最终将找到替代品。这也适用于铬酸盐,虽然它们表现良好并且过去已广泛用于机动车辆,但是毒性很大。
由于挥发性碳氢化合物会导致对流层污染,因此需要具有较低有机溶剂含量的涂料。实现这一目标的途径包括:
水性聚合物(乳胶漆)
固含量较高的聚合物(使用较少的溶剂)
粉末涂料
现在可以使用水性光泽涂料,但涂料的初始光泽度通常不如有机溶剂型涂料那么高。客户的选择是在高性能产品和更环保产品之间。激烈的研究工作不断改进这些涂料。
High solids paints (solvent based) are now available, but not without cost and performance compromises. The relative molecular mass of the polymer resin is reduced to a maximum of about 1000 compared to 5000 in conventional paints. This allows the proportion of polymer to be increased from 20-30% to 40%, hence the term high solids. The main problem is the need to keep the viscosity low. As the amount of solids increases, so does the viscosity, to the point where the paint cannot be applied properly. A lower proportion of solvent tends to slow down the drying and film hardening process, so the structure of the polymer changes - increased branching tends to reduce viscosity for the same molecular weight. The application of paint is more difficult. If using an aerosol, the paint needs to be under pressure. Sometimes paint is hot. It is very difficult to get a good look with high solids coatings.
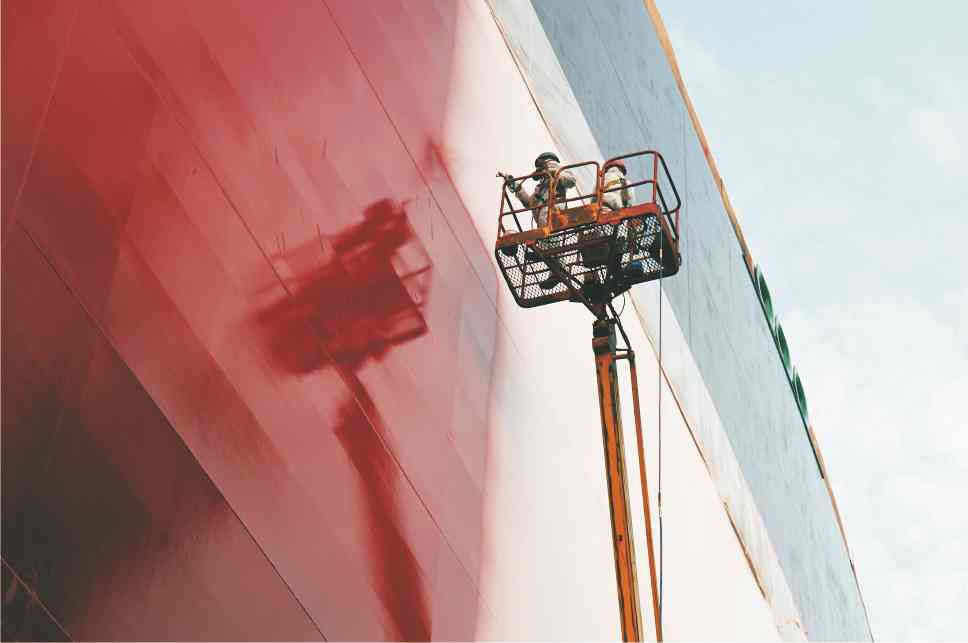
Figure 5 Spraying a boat in dry dock. The lower part is usually coated with coatings containing silicone (unit 68) or fluoropolymers (unit 66), which prevent barnacles from adhering to the boat, thereby reducing friction and thus reducing energy costs. Polluted ships can increase fuel consumption by 40%. |
|
Powder coatings are especially used on goods such as bicycles and white goods (refrigerators, washing machines). Powders consist of a resin (usually epoxy), pigments, catalysts and additives that promote crosslinking when the powder is heated. The powder is sprayed onto the article using an electrostatic Spray Gun and cured with heat to create a hard coat. More recently, acrylic powder coatings have been introduced as clear coats on car bodies. While a desirable solution for many applications, curing is achieved in an oven at high temperatures and is therefore not universally applicable (e.g. painting of wood and plastics).



