Viscometers measure the viscosity and fluidity of fluids. Viscosity comes from the internal friction of a fluid and is defined as a liquid's resistance to flow or shear stress.

Application of viscometer
Viscometers are used in a wide range of applications in materials science and the chemical industry for materials such as petroleum, asphalt, plastics, waxes, paints, coatings and adhesives. They are also used in food and beverages and personal care products such as cosmetics, shampoo and toothpaste.
Measuring viscosity is important when considering process conditions for materials that need to be pumped or piped. Viscosity also affects dipping and coating properties, which is of particular relevance to paints and inks.
Viscosity is a very useful indirect measure of material properties, including molecular weight and density, both of which affect flow behavior. Therefore, viscometers can be used to monitor batch consistency and quality control.
Example applications include:
Measuring the flow rate of engine oil under different temperature conditions
Analyze the flow characteristics of milk and design suitable piping systems
Check the viscosity of jams and syrups to ensure batch consistency.
Since changes in viscosity reflect changes in molecular weight, viscometers are used to characterize plastics. They are particularly useful in polymer synthesis, as flow rate can be used to determine the change in polymer length through different methods.
In many industrially useful cases, viscosity decreases with increasing enzyme activity. Viscometers are used to measure the activity of enzymes such as cellulase, protease, amylase and pectinase.
Types of viscometers
There are many ways to measure viscosity, but they fall into two basic methods. Objects, such as spheres or rotor blades, move through stationary material, or material flows over or past stationary objects. In either case, flow resistance is measured.
Capillary Viscometer
Capillary viscometers, also known as U-tube or glass viscometers, are commonly used in laboratory settings. Viscosity is measured by calculating the time it takes for a transparent or translucent fluid to flow between two points in a capillary.
For opaque liquids, it is difficult to determine when the sample passes a point in the tube, thus requiring the use of a counterflow viscometer that wets only the timed portion of the viscometer capillary during the actual measurement. Cannon-Fenske opaque, Zeitfuchs Cross-Arm, and BS/IP/RF viscometers from CANNON Instrument Co. (Pennsylvania State College; www.cannoninstrument.com) are all reverse flow types. Reverse flow viscometers need to be cleaned, dried and refilled before repeated measurements can be taken.
Capillary viscometers can be manual or automatic. Automatic instruments use infrared optical sensors for transparent samples, or thermal sensors for opaque samples.
Rotational Viscometer
简单的旋转粘度计,也称为Brookfield型粘度计,使用扭转弹簧来测量旋转材料中的心轴所需的扭矩。改变转子速度和尺寸允许测量不同的粘度范围。

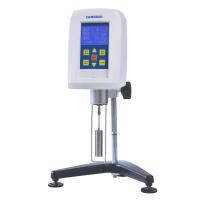
图1 - 安东帕的SVM 3000 Stabinger粘度计测量油和燃料的动态粘度和密度。
所述 SVM 3000(图1从)安东帕(阿什兰,VA; www.anton-paar.com)使用动力粘度仪测量原理。轻质磁性转子漂浮在充满液体的管中,管以恒定速度旋转。样品流体的粘性力驱动转子,导致平衡转子速度,记录为流体粘度的量度。
在流变仪中使用不同的主轴几何形状,例如圆柱形,同轴圆柱形,平行板和锥形板,以产生不同的剪切力。流变仪是比粘度计更复杂的仪器 ,用于测量非牛顿流体中与流速相关的粘度。
滚球,落球,球体和活塞式粘度计
所述 洛维斯2000 M / ME从安东帕是基于滚球原理的微粘度。球滚过封闭的,填充样品的毛细管,该毛细管以限定的角度倾斜。电感式传感器确定球在两个标记之间的滚动时间。
以类似的方式,落球或球形粘度计测量球或球在重力作用下通过倾斜一定角度的样品填充管所需的时间。落下的活塞式粘度计以类似的原理运行,但它们测量活塞落入材料的阻力。
购买粘度计的注意事项
选择粘度计是一个复杂的过程,取决于样品类型,粘度,不透明度,样品的可用体积,所需的通量和所需的自动化水平。至少应考虑以下因素:
粘度范围
准确性
温度控制
样本量和微量容量
自动化和计算机接口
法规要求和行业标准。
粘度范围
粘度以帕斯卡秒(Pa·s)测量,换言之,达到给定流速所需的压力量。粘度通常以厘泊(cP)表示,这是ASTM国际标准机构使用的单位; 1 cP等于1 mPa·s。20℃的水具有1.002cP的动态粘度。运动粘度是动态粘度与密度的比值; 测量单位是斯托克(St)。
Thermo Scientific Gilmont落球式粘度计(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA; www.thermoscientific.com)提供了一种简单,准确,经济,非常的方法,用于测量高达200 cP的透明液体粘度。
来自Malvern Instruments(英国Malvern; www.malvern.com)的Viscotek DSV 使用压力传感技术直接测量稀释聚合物溶液的相对粘度,粘度范围<1 mPa·s至20 mPa·s。
在大多数玻璃毛细管粘度计中,样品在重力作用下流动,但真空粘度计可用于测量高粘度材料。
真空粘度计需要非常精准控制的真空以将液体拉过毛细管。CANNON数字真空调节器(DVR)可与真空粘度计配合使用,ASTM D 2171在60°C(140°F)下测量沥青水泥。
旋转粘度计的扭矩范围决定了仪器可以测量的粘度范围。来自Brookfield工程实验室(马萨诸塞州Middleboro; www.brookfieldengineering.com)的 High Shear CAP-2000 +提供扭矩范围选择,标准扭矩为181,000 dyne·cm或低扭矩7970 dyne·cm。旋转速度在5至1000rpm之间变化,导致粘度测量范围为0.2-15,000cP。
准确性
粘度计的精度不仅取决于仪器本身的工程设计,还取决于温度控制的精确程度。通常进行重复粘度测量,将其平均以获得具有相关精度的结果。
粘度标准用于检查粘度计的准确度,对于验证是否符合行业质量体系非常重要。检查制造商是否提供适合您应用的标准。Brookfield有机硅和矿物油标准提供的流体粘度值恒定在25°C。该公司建议每年更换粘度标准。
温度控制
大多数材料的粘度随着温度的升高而降低。诸如发动机油之类的材料在使用中经受常规温度变化,并且在不同温度下需要测量粘度。因此,对粘度计进行准确的温度控制非常重要。
该 黑珍珠粘度计从CANNON仪器有限公司拥有内置的Peltier温度控制所有的测量系统。有些系统可以选择添加冷却设备,温度范围低于0°C。
样本量和微量容量
样品体积对于生物样品很重要,特别是在临床实验室中。的 SV-A系列从A&d称重(圣何塞,加利福尼亚; www.andonline.com/weighing)允许任意2毫升小以1%的精度的样本量的精准测量。CANNON仪器公司的Cannon-Manning半微量超低变U管粘度计。用0.5毫升的样品测量运动粘度。

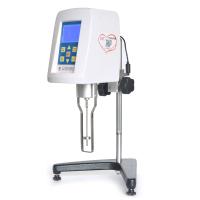
图2 - Brookfield Engineering的DV2T粘度计具有5英寸的特点。彩色显示,引导用户完成测试创建和数据采集。
自动化和计算机接口
简单的粘度计一次只允许一次测量,但对于连续测量或不同温度下的测量,有一个自动化系统是很有用的。 半自动运动粘度系统从UIC公司(Joliet的,IL; www.uicinc.com)可以同时和独立地确定最多12种样品的粘度。
一些自动化仪器可以连接到PC。如果需要,检查制造商的软件是否可以与您的内部实验室系统连接。
A&D Weighing的 WinCT-Viscometer软件使用RS232C接口在PC上实时显示SV系列正弦波振动粘度计的测量进度。可以保存或分析测量结果。
所述 DV2T粘度计从布鲁克菲尔德工程实验室(图2)提供一个5英寸 彩色显示,引导用户完成测试创建和数据采集。可以使用Program Generator软件创建多步测试协议,并通过USB闪存驱动器上传到DV2T。可以打印测试数据或将其发送到PC。
法规要求和行业标准
确保您选择的粘度计符合您所要求的ASTM或ISO行业标准。
Thermo Fisher Scientific的 C型Thermo Scientific HAAKE落球式粘度计测量透明牛顿液体和气体的粘度。它符合ISO 12058标准,并被接受为官方参考工具。
The PolyVISC Automatic Glass Capillary Viscometer is a benchtop unit for viscosity analysis of dilute solution polymers. Both transparent and opaque samples can be measured with the accuracy required by ASTM D 2857.