Similar to steel, concrete is often roughened prior to application of a paint system to enhance cohesion and help maintain adhesion of applied paint while in use. According to Appendix A7 of the SSPC Joint Surface Preparation Standard SP 13/NACE No. 6, Surface Preparation of Concrete, the required surface profile depth depends on the coating system to be used and the manufacturer's recommendations. Factors that may affect the chosen profile include: tensile and shear strength of the concrete and coating system; adhesion of the coating system to the concrete; internal stresses (i.e. shrinkage) developed in the coating system during application and curing; Differences in coefficient of thermal expansion between coating and concrete; modulus or stress relaxation properties of the coating system; thermal and chemical exposure environments; and coating thickness. Clearly, it is important to quantify surface profile depth in specifications and verify it prior to coating.
The method of quantifying the depth of a concrete surface profile is different from the method used to measure the surface profile on a metal surface. Historically, concrete surface profile (CSP) chips prepared by the International Concrete Repair Institute (ICRI) were used to assess the roughness of the prepared concrete visually (or tactilely) by comparing it with sandpaper of specified grit, and/or pass a mutually agreed surface roughness standard [1]. All of these methods are considered qualitative rather than quantitative. This article describes the standards and methods that can be used to determine the surface roughness of prepared concrete, including quantitative methods.
ICRI Guidelines 310.2-1997 (formerly 03732),
Selecting and specifying concrete surface preparations for sealers, coatings and polymer overlays
ICRI Guideline 310.2 deals with concrete surface preparation methods. While the guidelines focus on concrete floors, some methods work on vertical and elevated surfaces as well. The guide also includes 10 concrete surface profile (CSP) chips, which are copies of profile types (surface roughness) created by various surface preparation methods. The texture of the specimens ranges from very smooth (typically acid etched (CSP1)) to very rough (eg jackhammer) (CSP 10).
ASTM D7682, Test Method for Reproducing and Measuring Concrete Surface Profiles Using Replicating Putty
The method is designed to be used in conjunction with the ICRI CSP chip and provides the user with a long-term record of the concrete profile, as well as a method of indirect quantification of the surface profile from an imitation putty disk. It describes two methods (A and B).
对于方法A,使用仿制的腻子(如下所述)来获得粗糙混凝土表面的仿制试样,然后将其与十个ICRI CSP芯片或特定于项目的标准目视比较。
复制油灰可用于垂直,水平或高架表面。混凝土表面需要清洁干燥。塑料环用于测量组分A和B的等份,然后将它们手工混合(戴手套的手指/拇指)35-40秒,直到获得均匀的颜色。然后将混合物作为中间的土墩放在塑料腔(TCP)中,然后牢固地推入混凝土表面3到5秒钟(请参见下图),然后使其静置2-3分钟(低温)可能需要额外的固化时间才能固化环氧腻子)。确认油灰凝固后(可用手指压力测试型腔周围的多余油灰),将型腔从表面移开,但油灰将保留在表面上。将油灰盘从表面上剥下,并将该盘保留为长久记录。
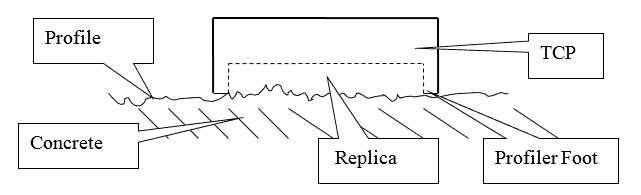
对于ASTM D7682中的方法B,随后使用专门设计的千分尺测量为方法A制备的仿制腻子试样,以获得表面轮廓深度的定量测量值。对于每个复制样在不同位置至少要获得十个微米的测量值,以确保在谷底进行一些测量,并在峰顶进行一些测量。从最高厚度测量值中减去最低厚度测量值,以确定每个复制试样的轮廓范围。
直接测量混凝土表面轮廓
需要深度千分尺,该深度千分尺装有以60°夹角加工的尖端的远距离尖头探针,尖端的标称半径为500 µm(20密耳)。探头的底部直径应在20到25毫米(0.8到1.0英寸)之间。探针的底部放在表面轮廓的峰顶上,而从探针表面伸出的弹簧式尖端则以最小的75g力伸入谷底。尖端相对于峰顶突出到谷底的距离以数字方式显示。由于准备好的混凝土的表面轮廓深度可能很大,因此深度千分尺的最小上限需要为6毫米(250密耳)。在编写本文时(2019年4月),ASTM标准草案描述了以下过程:
步骤1:在每个使用周期之前,通过测量通常由仪器制造商提供的,放置在平板浮法玻璃上的已知厚度的金属垫片,来验证仪器的准确性,然后通过将其探头放在一块平板浮法玻璃上来验证量具读数为零(零板)。如果仪器未正确读取垫片或玻璃板,量具制造商会提供调整说明。
Step 2: Hold the probe firmly on the prepared substrate to take rough concrete readings without having to drag the probe across the surface between readings, or the spring-loaded tip could wear out, causing false readings. Avoid holes and other surface irregularities that can produce false readings. Profiles are measured at enough locations to characterize the surface. Calculate the range and average for each location, and for all locations, in microns (µm) or mils (0.001 inches).
Summary
The surface profile of prepared concrete surfaces can be qualitatively assessed using the ICRI Concrete Surface Profile (CSP) chip (with or without replica discs made using a proprietary epoxy putty) and peaks can be measured using a specially designed micrometer Quantitative evaluation of the valleys of the replicated disc (indirect measurement of surface profile) for quantitative evaluation, or using a depth micrometer on the actual concrete surface (direct measurement of surface profile). Results may vary when measuring using each of these techniques, so it is important to specify/use only one method in a single project to avoid potential disputes.















