Brinell hardness testing is a non-destructive testing method that determines the hardness of a metal by measuring the size of the indentation left by an indenter. Under the specified ball diameter and test force, a large indentation left by the Brinell Hardness Tester on the surface indicates that the material is soft. The indenter on the Brinell Hardness Tester is spherical and leaves a circular indentation on the material being tested. The indenter is usually made of tungsten carbide.
required equipment
Brinell microscope
Brinell Hardness Tester
header
Description of Brinell Hardness Tester
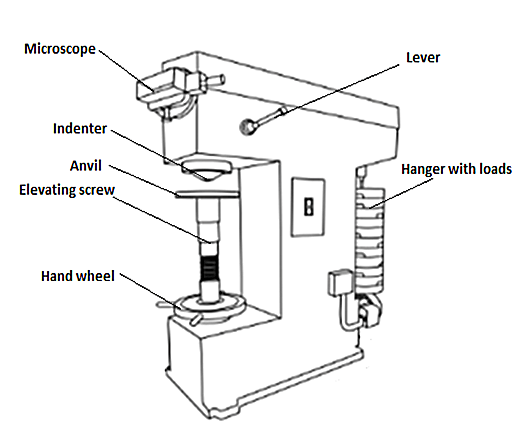
The Brinell Hardness Tester has a loading system consisting of a piston, weights, hydraulic buffer and plunger enclosed in the iron body of the machine. The material to be tested is placed on the anvil, which can be raised with screws. A spherical indenter is lowered onto the material with a specified force to determine the load on the specimen.

how the test works
This test consists of pressing a steel ball of diameter "D" into a test specimen under a load "P" for a specified period of time and measuring the average diameter "d" of the indentations left on the surface after the load is removed. The Brinell Hardness Number (BHN) is then calculated as the load divided by the surface area of the indentation.
The indentation depth (h) is determined by the following formula:
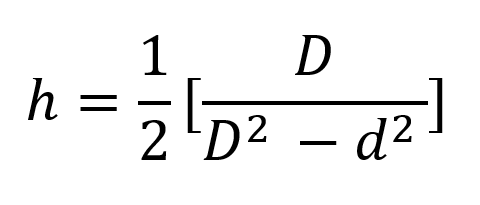
Then, use the following formula to determine the Brinell hardness number:
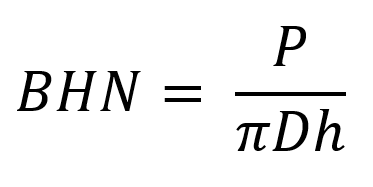
D = ball diameter, unit: mm
P = applied load, unit: kg-f,
d = indentation diameter, unit: mm.
Testing requirements
1. Before testing, the surface of the test material needs to be effectively cleaned.
2. Select the appropriate indenter for testing.
3. Shake the test bench to the set raised position.
4. Hold the load on the sample for the exact specified time, then release it.
5. The sample was taken out and the diameter of the indentation formed thereon was measured using a Brinell microscope.
Testing Standard
ASTM E10
JIS Z 2243
ISO 6506
Application field
The Brinell Hardness Tester's wide range of test forces means it can be used on almost any metallic material. Part size is limited only by the capacity of the test instrument. Since this is a non-destructive testing method, the samples tested can usually be returned to service.













