The working principle of the Hardness Tester is to directly measure the hardness of the tested material and the workpiece according to the principle of elastic impact. It is mainly composed of two parts: the impact device and the display device. The Leeb hardness test method is a dynamic hardness test method. This article mainly explains its working principle, and the tungsten carbide ball head and diamond ball head of the Leeb Hardness Tester in the verification regulations of JJG747-1999 "Leeb Hardness Tester" The verification method and the standard device used for verification are discussed.
0 Preface
The Hardness Tester consists of two parts, the impact device and the display device. It is used to directly test the hardness of the measured material and workpiece according to the principle of elastic impact. It is mainly used to determine the hardness of metal materials; it is suitable for large workpieces that are not easy to move and large parts that are not easy to disassemble. and hardness testing of components.
The Leeb hardness test method is a dynamic hardness test method, using the impact device of the Hardness Tester to impact the impact body (tungsten carbide or diamond ball head) on the surface of the sample, and measure the impact velocity at the point where the ball head is 1mm away from the sample surface and rebound speed, the ratio of the two is the Leeb hardness value.
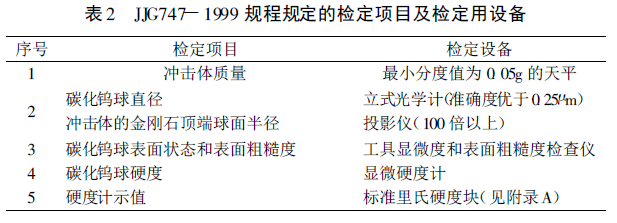
JJG747 -1999 "Leeb Hardness Tester" Verification Regulations were promulgated and implemented in 1999. The main technical requirements include impact device, display device, indication error and repeatability verification of Hardness Tester. For the ball head of the impact body, it is divided into two types according to the material type: tungsten carbide ball and diamond ball head, and the corresponding verification methods are given according to the ball head of different materials. As a person who has been engaged in metrological verification for a long time, the author has done in-depth exploration and thinking in the actual verification process, and gained some experience from it. This article discusses the verification methods of the two ball head diameters with you.
1 Discussion on the verification method of tungsten carbide ball diameter
JJG747-1999 "Leeb Hardness Tester" Verification Regulations describes the verification method of tungsten carbide ball diameter as: using a vertical optical meter (Table 4 in the regulations: the accuracy is better than 0.25μm) for verification, and the verification time is not less than It is carried out at three positions, and the difference between the measured value at any position and its nominal value shall meet the requirements of 2.2.2.
In the description of the above verification method, the author believes that the following two aspects are worthy of discussion:
(1) In the content expression of "the test is carried out at no less than three positions, the difference between the measured value at any position and its nominal value": "at no less than three positions" and "at any position "It is easy to cause confusion, whether it can be directly changed to "the difference between the measured value and its nominal value when the test is carried out at no less than three positions".
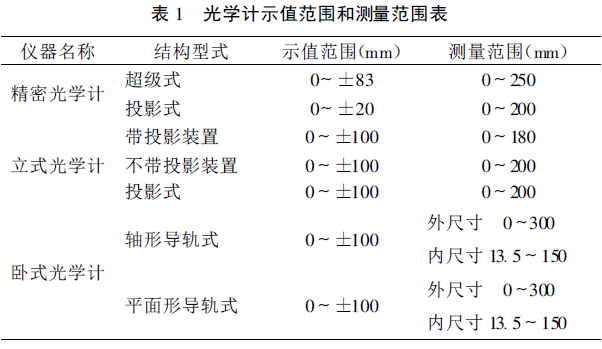
(2) It is stipulated in the regulations that the radius of the tungsten carbide ball head is 3.0mm, and the standard used for verification is a vertical optical meter. According to the verification regulations of JJG45-1999 "Optical Meter", the indication range and measurement of the vertical optical meter for measurement range table
As mentioned above (as shown in Table 1), the indication range of the vertical optical meter is ±100 μm, so it cannot be directly measured, and the diameter measurement needs to be carried out by the comparison method. For this reason, whether the standard should be added to the listed standard --- four equivalent blocks.
Table 1 Indication range and measurement range table of optical meter
2 Discussion on the diameter verification method
JJG747-1999 "Leeb Hardness Tester" test procedure describes the diamond ball head test method as follows: project the diamond top spherical surface of the impact body on the projector and compare it with the special curve plate, make the impact body rotate around the axis, and compare them respectively. The difference between the spherical radius on the two axial sections within 0.2mm from the top of the diamond and the standard radius should meet the requirements of 2.2.2.
In the description of the above verification method, the author believes that the following two aspects are worthy of discussion:
(1) Increase the technical requirements for the verification equipment used
① Verification equipment: special curve plate
②Verification equipment: projector (more than 100 times)
For a ball with a radius of 3.0mm and a tolerance of ±0.1mm, and it is compared with a special curve plate, the author thinks that the two parameters of confirming the correctness of the magnification of the projector and the maximum allowable error of the special curve plate should be more accurate. It is effective; and the magnification of the objective lens can be selected appropriately. Generally, it is better to take the radius of the rotating screen after imaging (1/2 to 2/3).
(2) Use other verification methods whose accuracy level is better than the method described in the regulations
Using a multifunctional tool microscope to measure the chord length and corresponding height of the spherical cross-section arc, calculate the corresponding diameter by the bow height chord method, and then divide it by 2 to get the radius value; this method is simple and accurate, and the author thinks it is more effective reference value.
4 Summary
The above is the author's introduction to the verification regulations of the Leeb Hardness Tester. It is favored by more and more users because of its small size, light weight, high precision, and the fact that it can be applied in any direction without using a workbench. It has been more than ten years since the JJG747-1999 "Leeb Hardness Tester" verification regulations were promulgated, to a certain extent, they are out of touch with the current needs, and have a great impact on the development of the measuring instrument. The trend of revising the verification regulations is unstoppable.
Yao Jingjing's "Discussion on the Verification Regulations of Leeb Hardness Tester"















