Falling body viscometers include falling ball type, falling column type and rising bubble type, and their principles are basically the same, among which the falling ball type is more common. This article mainly introduces the working principle and structure diagram of the falling ball viscometer.
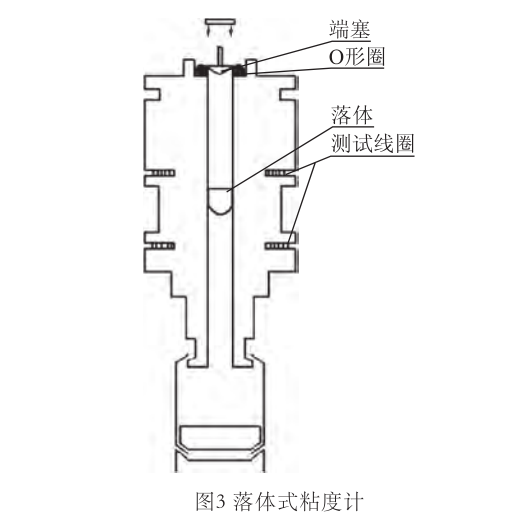
The basic principle of the falling ball viscometer is as follows: Put a sphere (glass ball, alloy ball, steel ball, etc.) into a viscous liquid at a certain temperature. , the resistance of the sphere to the liquid also increases, gradually approaching the force that makes the sphere fall, and when the force reaches a balance, the sphere will fall at a uniform speed. Since the resistance on the sphere mainly comes from the viscosity of the liquid, according to Stokes' law, the viscosity expression of the fluid can be deduced:

In the formula:
η is fluid viscosity;
d is the diameter of the steel ball;
ρ0 is the density of the steel ball;
ρ is fluid density;
g is the acceleration due to gravity;
l is a certain distance for the steel ball to fall at a uniform speed;
t is the falling time of the steel ball within the distance l;
fw is the correction factor for pipe wall effects.
In addition to the vertical falling ball viscometer, there is also a commonly used inclined falling ball viscometer, also called the Hoppler viscometer. Its viscosity tube is inclined, and the ball slides along the tube wall, so the force changes, and the tube wall effect needs to be considered, but the basic principle is similar to that of the vertical falling ball viscometer. Hoppler viscometer has precise structure, wide measurement range, convenient use and accurate measurement data. It is suitable for viscosity measurement of various fluids, especially non-Newtonian fluids.
The falling ball viscometer has a simple structure and is easy to operate. It can quickly provide measurement data and can measure a wide range of shear stress, which is beneficial to the control of the production process and the study of the structure and properties of the solution. The current falling ball viscometer can even measure Fluid viscosity, a wide range of applications. Its viscosity measurement range is limited, roughly 1~10 5 mPa•s. Due to the limitation of the specific gravity of the falling body, it can only measure the viscosity at a low shear rate, and cannot simulate the high shear rate in the actual situation. In addition, the measurement results of the falling body viscometer will be affected by factors such as the falling trajectory of the ball and the uniformity of the sample tube, so there is a certain degree of uncertainty.

