In the application, the dispersant is mainly used to improve the stability of the pigment dispersion suspension, while the wetting agent is used to improve the wetting and dispersibility of the pigment, which is the so-called grinding aid. In other words, the secondary aggregates and adsorbents on the surface of the aggregates and in the voids during grinding must be replaced by wetting agents, and the affinity between particles and base materials can be increased by wetting agents. The interface of the crushed new particles is protected by a dispersant. The dispersant is adsorbed on the surface of the new particles to reduce the surface energy and prevent re-agglomeration.
Pigment wetting mechanism. Wetting is the process of changing the surface properties of pigments. It is to remove water and air adsorbed on the surface of pigments, change its polarity, reduce the interfacial tension between liquid and solid, and increase the affinity between pigments and paints . Humectants are auxiliary agents that work at this stage. It is extremely sensitive to the surface of the pigment
Strong affinity. Practice has proved that if the molecular weight of the resin polymer or the added wetting agent in the paint is too high , the wetting ability will be significantly reduced, that is to say, good wetting effect cannot be obtained with high molecular weight dispersant, and only better stability can be obtained. Similarly, a wetting agent with a small molecular weight can achieve a good wetting effect, but not a good stabilizing effect. Because the pigment wetting efficiency is affected by the following factors: the geometric shape of the pigment particles; the surface characteristics of the pigment particles; the surface treatment viscosity of the dispersion medium; the void volume of the pigment secondary particles; additives; resin paint polymer activity, etc.
Washborne proposed a formula for wetting efficiency based on the above factors:
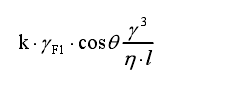
In this formula, k is a constant, γ F1 is the interfacial tension of the base material, θ is the base material/pigment interface contact angle, γ is the gap radius of the pigment particles, l is the length of the pigment particle gap, and η is the viscosity of the base material. The factors listed in this formula that affect wetting efficiency are basically fixed in a given mill paste formulation except viscosity . Reducing viscosity increases wetting efficiency, but there is a limit to the reduction in viscosity. Adding a wetting agent to reduce the solid/liquid interfacial tension, reduce the contact angle, and increase the cos θ value is also one of the methods to improve the wetting efficiency.
Selection and application of wetting and dispersing agents. The base materials used in coatings are divided into two categories: non-polar and adsorption active. Acrylic is a non-polar resin base material with very low adsorption activity, and the pigment has a low affinity to the resin. Wetting and dispersing agents should be used to change the surface characteristics of pigment particles, enhance the lyophilicity of pigment particles, and increase the wetting ratio. The adsorption layer formed by the resin and additives on the surface of the pigment improves the storage stability of the paint. Choose a wetting and dispersing agent with good compatibility with the resin.
In the base material containing adsorption active groups, the resin itself has more active groups, which can be adsorbed on the surface of the pigment and act as a surfactant. Wetting and dispersing agents for pigments are generally added during batching to make them adsorb on the surface of the pigments during the grinding and dispersing process. The most satisfying thing is to try to make more resin and a certain amount of additives adsorb on the surface of the pigment together.






