In the screen printing process, there are several key working objects, namely screen printing plates, scrapers, inks, printing tables and substrates . The screen printing plate is placed on the printing table, and the ink is transferred to the substrate through the mesh of the screen printing plate under the pressure of the scraper to form printed patterns and characters. The ink is squeezed from the mesh of the printing area to the substrate by the scraper during the moving process . The contact between the scraper and the substrate is always a linear contact during the moving process, and the contact line also follows the movement of the scraper. Move; when the scraper moves from one end of the screen to the other, the scraper should be lifted, and at the same time, due to the resilience of the screen, the screen will also be separated from the substrate, and the printing table will return to the original position of ink and substrate position; this whole process is a complete printing stroke. Figure 1-16 is a schematic diagram of screen printing operation.
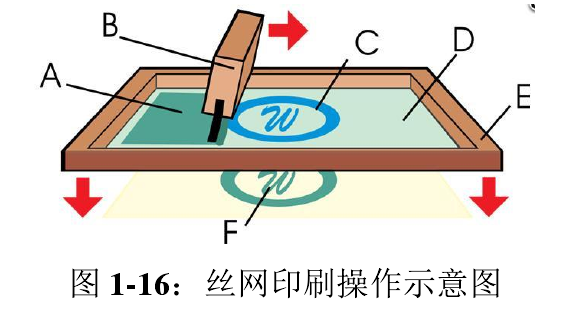
Resilience refers to the reaction force of the screen to the scraper due to its own tension during the printing process. In order to allow the ink to pass through the mesh more smoothly, it is necessary to maintain a certain gap between the screen printing plate and the substrate. The part of the screen that is in linear contact with the scraper will be squeezed to the surface of the substrate under the action of pressure. When the scraper leaves that area, the screen itself will leave the surface of the substrate again under the action of the rebound force due to the disappearance of the pressure. The existence of resilience can ensure that the screen area outside the contact of the squeegee is separated from the substrate during the printing process, avoiding inaccurate printing size and contamination of the substrate.
