Newtonian fluids, non-Newtonian fluids, rheology, thixotropy, dilation... What is the difference between these liquid properties? Remember: what does it matter? Here's what you should know if you're sizing or choosing a pump, mixer, or other device that applies shear to a fluid. All fluids can be divided into two basic types, Newtonian and non-Newtonian.
Newtonian fluid
The viscosity of a Newtonian fluid remains constant regardless of the amount of shear applied at a constant temperature. These fluids have a linear relationship between viscosity and shear stress.
for example:
water
mineral oil
gasoline
alcohol
non-newtonian fluid
As you might guess, non-Newtonian fluids are the opposite of Newtonian fluids. When a shear force is applied to a non-Newtonian fluid, the viscosity of the fluid changes. The behavior of fluids can be described in one of four ways:
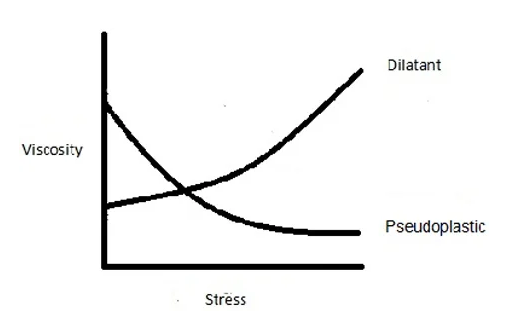
Swelling - The viscosity of a fluid increases when a shear force is applied. For example:
quicksand
cornmeal and water
Plasticine
Pseudoplasticity - Pseudoplasticity is the opposite of dilatancy; the more shear force is applied, the more viscous it becomes. For example:
ketchup
This graph shows how viscosity changes relative to the amount of shear or stress applied to the fluid.
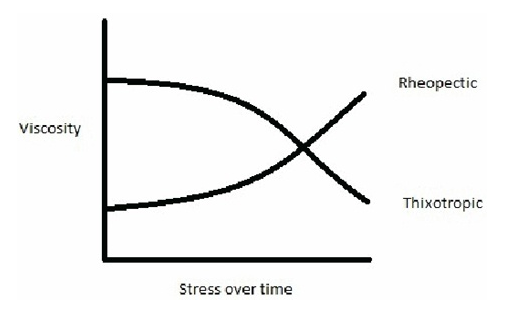
Rheological - Rheological is very similar to bulking agents in that viscosity increases when shear is applied. The difference here is that the viscosity increase is time dependent. For example:
plaster paste
cream
Thixotropy - Thixotropic fluids decrease in viscosity when shear is applied. This is also a time-dependent property. For example:
coating
cosmetic
asphalt
glue
This graph shows how viscosity changes over time as it is applied to the fluid.
Why do you need to know the difference? It is important to have a good understanding of the properties of the fluids to be transferred, mixed or pumped, as viscosity plays a large role in selecting and selecting equipment. Knowing how it responds to shear will help you properly size and select any equipment it will come in contact with.