Answer: Since the entire curing process of the paint in the furnace needs to go through two processes: the physical drying process (to evaporate the solvent) and the chemical drying process (to polymerize or cross-link the organic matter of the paint), the temperature setting in the furnace is usually It is divided into three sections: physical drying section - solvent evaporation, physical -chemical drying transition section - effective solvent evaporation and organic solidification, chemical drying section - organic polymerization or crosslinking occurs when the organic matter reaches a certain temperature.
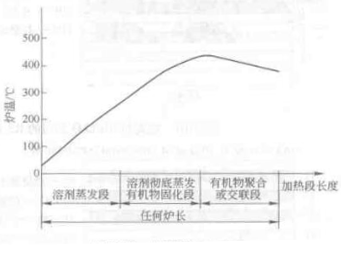
In the physical drying section and the transition section, the furnace temperature should rise slowly to allow the solvent to have sufficient time to evaporate and to separate from the solid content of the coating. If the temperature curve in this section is too steep, the solid content on the coating surface will advance Entering the drying or polymerization period, the solvent bubbles cannot be separated and the inner layer boils and ruptures, and the surface of the dried coating will have rough pitting, which affects the surface quality. In the chemical drying section, the furnace temperature curve should first move up steadily according to the coating polymerization temperature, and then drop slightly. Because the coating organic matter still needs a hardening period after polymerization or crosslinking. Some people even think that the evaporation of the solvent in the first two stages is only 90%, and 10% of the solvent is still evaporating after the polymerization of the organic matter. If the furnace temperature drops to normal temperature immediately after the polymerization temperature, the coating is soft and the solvent is not complete. Evaporation will also produce pitting. Therefore, the decline of the curve in the chemical drying section cannot be too steep. Some people call this insulation section.

However, for some large-scale units, the furnace temperature setting does not follow the above rules, because the coatings they use are usually high quality. /min does not need to set up the preheating section and the holding section. The temperature of each section of the furnace is in the high temperature zone, that is to say, the furnace temperature curve is in a horizontal state, and the coating will not appear blistering or overheating aging. However, the price of this kind of coating is relatively high, and the unit with a production line speed below 100m/min is rarely used.
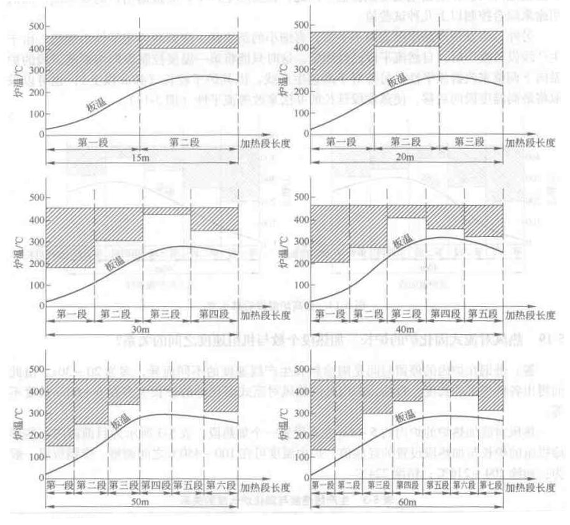
There is no standard curve reference value for temperature control. In the production process, the setting of the temperature curve should be comprehensively formulated according to the type of coating, the evaporation temperature of the solvent, the thickness of the coating, as well as the length of the furnace and the number of heating sections of the furnace, and through the adjustment in the experiment and actual production, Continuously summarize, and finally let the distribution of the temperature curve tend to be reasonable. Figure 5-13 is a set of substrates with a thickness of 0.5mm, the temperature of circulating hot air in the furnace is 120~400℃, the amount 50000-70000m 3 /h, and the curing time of the coating is 30s , When the wet film thickness of the coating is 40 ~ 45um, the corresponding temperature settings of several furnace lengths are suggested. During production, on the basis of measuring the temperature of the board, according to the actual temperature difference between the hot air and the board temperature, the speed of the production line and The figure and so on set the furnace temperature value, and adjust it according to the actual situation of the unit.