At 20°C, the viscosity of water is about 0.01P (0.001Pa·s), the viscosity of linseed oil is about 0.50P (0.050Pa·s), and the viscosity of castor oil is about 10P (1.0Pa·s). These three liquids are often used as reference liquids for visual viscosity determination. Generally, the viscosity of liquid paint when brushing is usually 1~3P (0.1~0.3Pas), the viscosity of the dry paint film is about 10 4 P (10 3 Pa s), and the viscosity of the dry paint film can reach the order of 10 9 , the viscosity of the glassy polymer reaches the order of 1012. Methods for accurately measuring viscosity include capillary method, rotational method and falling ball method, etc. Various methods are compared in Table 2-4.
| method | Experiment | Applicable conditions | equation |
| capillary method |
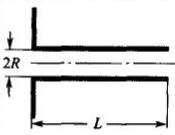
Capillary viscometer liquid flows from the capillary | γ: 10 -1 ~10 10 s -1 | η=πR 4 ΔP/8QvL In the formula, R——capillary radius P - pressure drop across the capillary Qv——volume flow rate L - capillary length |
| Rotation method |
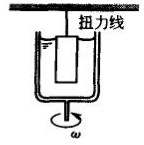
Liquid fills the gap between the two coppers | γ: 10 -3 ~10 3 s -1 viscous and highly viscous substances | η=KM/ω In the formula, K——instrument constant M——Rotational moment ω——rotational angular rate |
| falling ball method |
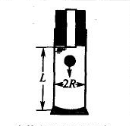
The liquid is packed in the viscosity tube | γ: 10 -2 s -1 (very small) | η= 2r 2 (ρ s -ρ l ) g/9v In the formula, ρ s——ball density ρ l ——colloid density r——ball density v - the final velocity of the ball motion g - acceleration due to gravity |
Sometimes in paint design and paint transportation, it is more convenient and practical to use kinematic viscosity than the above absolute viscosity. The kinematic viscosity is represented by v, which is the ratio of the absolute viscosity η of the liquid to the density p of the liquid, and the unit is St (Stokes) or cm 2 /s.