The adhesion between the coating and the substrate is very complicated, and it is difficult to explain the influence of the above-mentioned single factor, which is the result of the comprehensive effect of multiple factors. Through the analysis of the complex factors combining the above theory with the actual coating, the influencing factors of adhesion are obtained, and the important factors are as follows:
(1) The wetting condition of the substrate surface. To get good adhesion, the necessary condition is that the paint completely wets the surface . Usually, pure metal surfaces have high surface tension, and topcoats generally have low surface tension, so they are easy to wet, but the actual The metal surface is not pure, the surface is easy to form oxides, and can adsorb various organic or inorganic pollutants, which can greatly reduce the surface tension, thus making wetting difficult. The purpose of surface treatment is to improve the surface of the substrate. The surface energy is conducive to the wetting of the coating. For substrates with low surface energy, proper treatment is even more necessary.
(2) The adhesion of the coating film also has a certain relationship with the properties of the metal. The adhesion of the same coating on different metal surfaces is not the same. According to the size of adhesion, the metals are arranged as follows Nickel>steel>iron>copper>brass>aluminum>tin>lead
Therefore, when measuring the adhesion of the coating, in addition to measuring according to the standard method, it is also necessary to measure it on the material actually used.
(3) Paint viscosity. When the viscosity of the coating is low, it is easy to flow into the recesses and pores of the substrate, and a higher mechanical fitting Generally, the drying paint has better adhesion than the air-drying paint. At high temperature, the viscosity of the coating is very low. It is also one of the reasons.
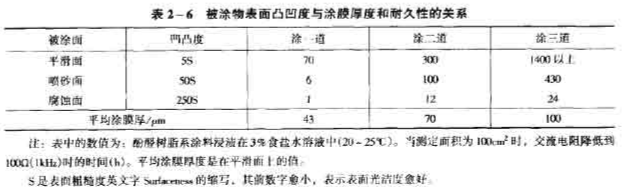
(4) Surface roughness. Appropriately increasing the surface roughness can increase the mechanical interlocking effect, and on the other hand, it is also conducive to the wetting of the coating on the surface of the substrate. However, if it is too rough, if the viscosity of the coating is high and the penetration performance is limited, there will be fine gaps, which will easily cause defects and cause adhesion decline. When the coating thickness is not large, the anti-seepage protection performance is reduced. Table 2-6 shows the effect of substrate roughness on the durability of the coating film.
(5) Film formers. The stronger the polarity of the macromolecular polar groups of the film-forming material, the more the number, and the greater the relative molecular weight, the more favorable it is for the film-forming material to form a stronger intermolecular force with the surface of the substrate, and the combination is firmer.
(6) The influence of internal stress. The internal stress of the energy film is an important factor affecting the adhesion. If the internal stress is too large, when it is greater than the cohesion of , the coating will crack; when it is greater than the adhesion of the coating, the coating will be damaged such as shelling and lose its protective effect. There are two : A. The shrinkage stress caused by the volume shrinkage of the paint during the curing and solvent volatilization of the paint; B. The thermal stress generated when the ambient temperature changes due to the different thermal expansion coefficients of the paint and the substrate. No matter what method is used to cure the coating, it is inevitable to have a certain volume shrinkage. The shrinkage can not only be caused by solvent volatilization, but also by chemical reactions. The volume shrinkage of polycondensation reaction is serious, especially for the curing process of polycondensation reaction with small molecules, because some of them will become small molecules and escape. When the double bond of olefin or oligomer undergoes polyaddition reaction, the two double chains change from van der Waals force bonding to covalent bond bonding, and the atomic distance is greatly shortened , so the volume shrinkage rate is also large, such as the curing process of unsaturated polyester Medium volume shrinkage up to 10%. During ring-opening polymerization, one pair of atoms changes from van der Waals effect to chemical bond, and the other pair of atoms changes from original chemical bond to close to van der Waals force, so the shrinkage rate of ring-opening polymerization is small, and the epoxy resin is cured The shrinkage rate during the process is low, which is the reason for the better adhesion of epoxy coatings. Reducing volume shrinkage in the curing process is of great significance to improving adhesion. Increasing pigments, increasing solid content, and adding prepolymers to reduce the concentration of functional groups in the system are common methods for coatings to reduce curing shrinkage. Adding inorganic fillers also has the effect of reducing coating. The role of film thermal expansion coefficient reduces thermal stress. In addition, the thicker the film, the greater the internal stress. In short, the internal stress of the paint film, the adhesion and the strength of the film are mutually competitive.
(7) The role of adhesion promoter (coupling agent). The active group of the coupling agent is used to form ionic or covalent bonds with the metal, and at the same time, it can interact with the functional groups in the coating film to generate chemical bonds to improve the adhesion performance. Between the epoxy coating and the base metal, polyacrylic acid (PA) is used to treat the metal (iron, copper, aluminum), and the adhesion between the metal and the epoxy coating on the polyacrylic acid structure and the metal A chemical action takes place, forming an ionic bond. It may also Therefore, the pre-treatment of the coated steel plate with polyacrylic acid emulsion can significantly increase the adhesion of the epoxy bottom knee containing glass flakes to the base metal.


