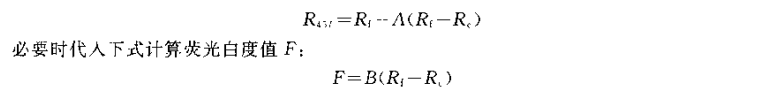In this method, the whiteness test result is expressed by the reflection factor (%) of paper and cardboard to blue light with a dominant wavelength of 457nm under D65 light source and diffuse/vertical illumination observation conditions. For samples containing fluorescent whitening agents, the fluorescent whitening effect, that is, the fluorescent whiteness, can also be measured and calculated. The determination of whiteness is divided into two parts: the test method of samples without fluorescent whitening agent and the test method of samples containing fluorescent whitening agent.
1. Determination of samples without fluorescent whitening agent
It is suitable for near-white paper and cardboard samples without fluorescent whitening agent.
1.1 Definition
(1) Reflection factor R.
(2) Internal reflection factor R.
(3) The blue light reflection factor R457 is the internal reflection factor measured with a reflectance photometer (Whiteness Meter) that meets the relevant regulations under the blue light condition of the dominant wavelength (457±0.5) nm.
1.2 Instruments
(1 ) The spectroscopic and geometric characteristics of the reflection photometer instrument are equivalent to the reflection photometer of 8.22.
(2) R4z filter ﹑ the filter matches the optical harmonic characteristics of the instrument's light source, lens, integrating sphere wall and receiver, and gives a spectrum with a dominant wavelength of (457 ± 0.5) nm and a half-wave width of 44 nm distribution characteristics.
(3) The working standard plate does not contain fluorescent whitening agent, and the reflection number is not more than 0.1%.
1.3 Preparation of samples
① Carry out sampling according to the standard method.
②Cut no less than 10 rectangular test pieces of 150 mm×75 mm from the extracted paper, and the total thickness should reach the level where the reflection factor does not increase with the increase of the number of layers. Each test piece is stacked in a stack with the front facing upwards, and a test piece is lined up and down for protection against contamination and unnecessary exposure to light or heat radiation.
1.4 Test steps
① According to the instrument manual. Connect the instrument and the light source, and after a period of stabilization, insert the R..-filter into the reflected light beam of the instrument, and calibrate the zero point and scale value of the instrument with the standard black plate and the working standard plate.
②Remove the protective layer from the sample stack, put the sample on the test hole, and test the reflection factor R:; of the uppermost: surface layer under D:; light source illumination, accurate to 0.1% reflection factor. Take off the top layer of sample and put it on the bottom of the paper stack, repeat the test of the reflection number of the second test piece, and then test no less than 5 test pieces sequentially in the same way. To test the reverse side, turn over the paper stack and repeat the above operation.
1.5 Calculation of test results
Find the arithmetic mean of the front and back samples R457, accurate to one decimal place.
2. Determination of fluorescent whitening agent
It is suitable for near-white paper and cardboard samples containing fluorescent whitening agent.
2.1 Definition
(1) Reflection factor R is the ratio of the radiant flux f reflected by an object to the radiant flux reflected by a fully reflective diffuser under the same conditions, expressed as a percentage.
(2) Internal reflection factor R. The thickness of the sample layer reaches the reflection factor when the reflection factor no longer increases with the increase of thickness.
(3) The blue light reflection factor R is the internal reflection factor measured under the blue light condition of the dominant wavelength (457±0.5 ) nm with a reflectance photometer (Whiteness Meter) that meets the relevant regulations.
Note: This value will be greater than 100% due to the additional blue light reflected by the fluorescent whitening agent.
(4) Reflection factor R, simulation D. The blue light reflection factor of the sample under the lighting conditions of the light source.
Reflection factor R, the blue light reflection factor of the sample under the illumination conditions that simulate the light source of D. but use a UV cut filter to remove the ultraviolet part less than 400 nm.
(5) The part of the reflection factor of fluorescent whiteness F that can be directly attributed to the whitening effect of the fluorescent whitening agent.
(6) Fluorescent whitening agent FWA is a powder that can cause visual whitening effect due to fluorescence in the blue range of visible light when it penetrates into or penetrates into a near-white base material.
2.2 Instruments
(1) The spectroscopic and geometric characteristics of the reflection photometer instrument are equivalent to the reflection photometer of 8.22.
(2) R457 filter This filter matches the spectral characteristics of the light source, lens, integrating sphere wall and receiver of the instrument. The spectral distribution characteristics of the dominant wavelength (457=:0.5) nm and the half-wave width of 44 nm are given.
(3) The UV cut-off filter can remove ultraviolet rays less than 400 nm, but has no obvious effect on the reflection factor of white non-fluorescent samples.
(4) In order to correct the reflection factor R of the sample containing the fluorescent whitening agent to the standard value R; for the three-level fluorescent standard whiteboard, a relatively stable fluorescent whitening agent is added to the whiteboard required.
(5) The third-level non-fluorescent standard whiteboard is made of the same material as the third-level fluorescent standard whiteboard, but no fluorescent whitening agent is added.
(6) The reflection factor of the standard black tube is not more than 0.1%.
2.3 Preparation of samples
① Carry out sampling according to the standard method.
② Cut out no less than 10 rectangular test pieces of 150mm×75mm from the extracted paper, and the total thickness should reach the level where the reflection factor does not increase with the increase of the number of layers. Each test piece is stacked in a stack with the front facing up, and a test piece is lined on the top and bottom for protection, preventing contamination and unnecessary exposure to light or heat radiation.
2.4 Calibration of the instrument
At present, there is no light source that fully matches the illuminant D defined by CIE. However, it is still possible for a standardized laboratory to calibrate the light source used to match the spectral power of the illuminant D; Therefore, as long as the standardization laboratory transmits the Mann value of the fluorescent standard plate and the corresponding non-fluorescent standard plate, the standardization of the measured value of the whiteness of the sample containing the fluorescent whitening agent can be realized by the following method, and the problem caused by the light source Test errors are minimized.
① According to the instrument manual, turn on the power switch of the instrument. After a period of stabilization, insert the Rs: filter into the reflected light beam, and calibrate the zero point and scale value of the instrument with the standard black cylinder and the three-level non-fluorescent standard plate respectively. Then put the !-level fluorescent standard plate in the test hole, and test the blue light reflection factor S under the illumination of the fully simulated D light source.
②Insert a UV cut-off filter into the incident light beam, calibrate the zero point and scale value of the instrument with the standard black bar and the third-level non-fluorescent standard again, put the third-level fluorescent standard in the test hole, and test the value under the condition of eliminating ultraviolet rays. Blue light reflection factor Se.
③ Calculate the calibration factors A and B from the calibration value IV of the blue light reflection factor of the third-level non-fluorescent standard plate and the calibration value s of the blue light reflection factor of the fluorescent standard plate:

2.5 Test steps
①Insert the Rr filter in the reflected beam, calibrate the zero point and scale value of the instrument with a standard black cylinder and a third-level non-fluorescent standard plate.
②Remove the protective layer from the sample stack, put the sample on the test hole, browse and test the full simulation of the top layer of sample D: the reflection factor R under the illumination of the light source, and the reading is accurate to 0.1% reflection factor. Remove the top layer of sample and put it on the bottom of the paper stack, repeat the test of the reflection factor of the second paper sample, and then use the same method to test no less than 5 test pieces in sequence. If you need to measure the reverse side, turn over the paper stack and repeat the above operation.
③Insert a UV cut-off filter in the incident light beam, calibrate the zero point and scale of the instrument with a standard black cylinder and a third-level non-fluorescent standard, and repeat the 2 operation, and test the reflection factor R of the sample under the simulated D65 light source to eliminate ultraviolet light. Accurate to 0.1% reflection factor.
2.6 Calculation of test results
Calculate the average R and the average R of the front and back of the sample respectively, and substitute the two average values into the following formula to calculate the blue light reflection factor, that is, the whiteness value R45.