The falling ball method uses the speed of solid matter flowing in the liquid to measure the viscosity . The instrument used is called a falling ball viscometer, which is suitable for measuring transparent liquid coatings with high viscosity, such as nitrocellulose varnishes and paints. It is mostly used in production control.
A simple falling ball viscometer consists of a glass tube of precise size, which is filled with the liquid to be measured. A small steel (or aluminum, glass) ball freely falls along the center of the tube, and a distance during the free fall is taken. Determination of its time, expressed in s. The seconds measured by the vertical falling ball viscometer can be approximately .
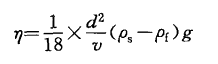
In the formula
d-the diameter of the steel ball, cm;
ν — the falling speed of the steel ball, cm/s;
ρ s- the density of the steel ball, g/cm 3 ;
ρf - sample density, g/cm 3 ;
g — Gravity acceleration, 980cm/s 2 .
my country's national standard GB/T 1723-1993 "Determination of Coating Viscosity" stipulates the specifications and test methods of the falling ball viscometer. The eccentric falling ball viscometer is an improved product of the falling ball viscometer, namely the Hoppler viscometer. Its characteristic is that the tube is inclined at a certain angle, so that the ball slides down steadily along the tube wall, which can avoid the measurement error caused by the ball's deviation from the vertical line during the vertical landing process; Silver gray spots can be reflected on the surface, so it can also measure the viscosity of opaque liquids.

