The physical or chemical change process of liquid Coating on the surface of an object from a fluid layer to a solid film is generally called film drying. The drying process can be divided into different stages according to the physical properties of the film, mainly the change process of viscosity. It is customary to divide it into three stages: surface drying, actual drying and through drying. American ASTM D 1640-2003 divides the drying process into eight stages. For the drying time, the requirements of the construction department are as short as possible, so as to avoid the coated workpiece being stained with rain, dew and dust, and the construction period can be greatly shortened; for Coating manufacturing, due to the limitation of the materials used, a certain amount of drying is often required. Time to ensure the mass after film formation. Due to the long time required for Coating through drying, only two items of surface drying (surface drying) and actual drying (hard drying) are generally measured.
(1) Determination of surface drying time
The commonly used methods are the cotton ball blowing method, the finger touch method [GB/T 1728- -1979 (1989) ] and the small Glass ball method (GB/T 6753.2--1986). The cotton ball blowing method is to put an absorbentcottonph ball on the surface of the film, and gently blow the cotton ball with the mouth in the horizontal direction. If it can be blown away without leaving cotton silk on the film surface, it is considered that the surface is drying. The finger touch method is to touch the surface of the film with the finger lightly. If it feels a little sticky, but no paint sticks to the finger, it is considered that the surface is drying or referred to as dry. The small Glass ball method is to pour about 0.5g of small Glass balls with a diameter of 125-250μm on the surface of the film at a height of 50-150mm. When the small Glass balls on the film can be gently brushed off with a brush without damaging the film surface, it is considered that the surface is drying and the time is recorded. Judge whether it is qualified according to the product regulations.
(2) Measurement of actual drying time
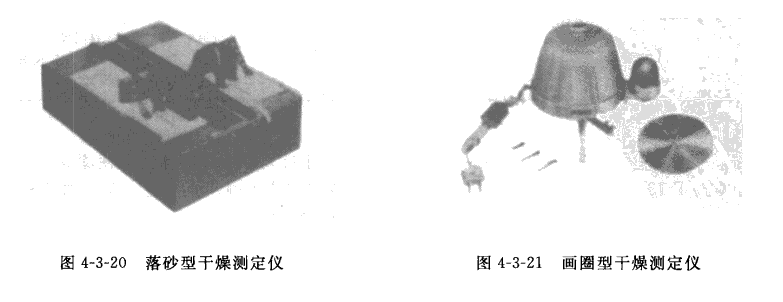
Commonly used pressure filter paper method, cotton ball method, blade method and thick layer drying method. My country's national standard GB/T 1728-1979 (1989) has detailed regulations. In the ISO 9117:1990 standard, there is a method for applying a load to a coat to determine the degree of through drying. The pressure filter paper method is to press a piece of qualitative filter paper on the film with a Drying Tester (shown in Figure 4-3-18), remove the Tester after 30s, turn the sample over and the filter paper can fall freely, that is, it is considered to be actually dry. Similarly, the cotton ball method uses 30s to remove the Tester and absorbentcottonph balls. If there are no cotton ball traces and loss of light on the film, it is considered to be actually drying. The blade method uses a safety blade, which is suitable for thick coating and putty films. Thick layer drying method is mainly used for insulating paint. The film drying time is affected by the temperature, humidity, ventilating, light and other factors of the surrounding environment, so the measurement must have a certain environment and equipment, and be carried out in a constant temperature and humidity room.
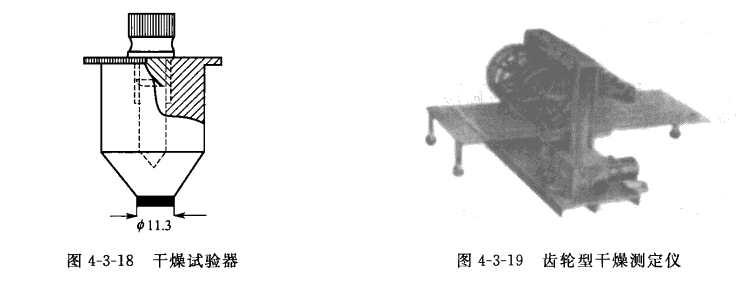
Since the drying of Coating and the formation of film are a very slow and continuous process, in order to observe the entire change in the drying process, an automatic drying time measuring device can be used. One is to use a motor to drive the gear through the gearbox and walk in a straight line on the film at a slow speed of 30mm/h, for a total of 24h. With the gradual drying of the film, the gear traces gradually change from deep to shallow until all disappear (Figure 4-3-19). The other is to use the motor to drive the funnel containing fine sand, move slowly on the film-coated template, and the sand will continue to fall on the film to form linear sand traces to measure the time required for different stages of drying (Figure 4-3-20). More professional ones use the needle tip to slowly draw a circle with a radius of 5cm on the film. It takes 24h to draw a circle, so that the drying degree of the film over time can be observed on a smaller test plate area (Figure 4-3-21).