Latex paint is made by mixing water-dispersed polymer emulsion and pigment water slurry.
1. Polymer emulsion
The polymer emulsion is composed of various vinyl monomers, in the presence of an emulsifier, initiated by a free radical initiator, and the emulsion polymerization obtains a polymer dispersion with a high relative molecular weight.
Such emulsions are divided into two types: thermoplastic and cross-linked emulsions. Thermoplastic emulsions such as polyvinyl acetate and polyacrylic acid emulsions have good performance after film formation due to their high molecular weight. The crosslinkable ones have reactive groups and can be crosslinked at room temperature or thermally cured to form a film. More than 90% of latex paints are thermoplastic, while a small amount of cross-linked emulsion paints are mainly used in metal finishing and protection.
Some polymer emulsions use emulsifiers to forcibly disperse cross-linkable resins with lower relative molecular weights in water to form resin emulsions. After the coating film is cured and cross-linked, the relative molecular weights are increased to give performance. Such as water emulsion of liquid epoxy resin, water emulsion of low molecular weight chlorosulfonated polyethylene resin, some polyurethane emulsion and alkyd resin emulsion, etc. Epoxy resin emulsions can be cured and cross-linked by modified polyamides, phenolic-amine adducts, polyurethanes, etc.; chlorosulfonated polyethylene resin emulsions can be cured and cross-linked by metal oxide vulcanization.
2. Pigment slurry
The latex paint can add corresponding coloring pigments, fillers and antirust pigments according to the application. due to polymer
The emulsion will destroy the stability of the latex under strong mechanical force, so the emulsion is not used as a vehicle for color (filler) material grinding. Usually, the pigment is dispersed in water with a pigment dispersant to make a pigment water slurry, which is then transferred into an emulsion to form a latex paint.
3. Coalescent
Latex coatings need to add film-forming aids, which are low-volatility organic co-solvents. During the film-forming process of latex coatings, co-solvents reduce the glass transition temperature of the resin, which is conducive to the deformation of micelles and promotes the fusion between colloidal particles. Make it form a continuous and uniform dense coating. Because it can reduce the film-forming temperature, so that the coating can form a good coating film at an ambient temperature lower than the glass transition temperature of the resin, it is called a film-forming aid.
4. Other additives
According to its characteristics, latex paints generally need to add thickeners to improve storage stability and improve construction performance; add defoamers to improve the appearance of the coating film; add polyols to improve freeze-thaw stability; Add a mildewcide. For metal latex primers, early "flash corrosion" phenomenon is easy to occur after coating, and corresponding "flash corrosion" inhibitors need to be added.
Latex coatings are divided into two categories: architectural latex coatings and metal latex coatings according to their uses. Latex coatings for construction are mainly used for interior and exterior walls and ground finishing; latex coatings for metal can be used as primers and topcoats for industrial maintenance coatings and certain mechanical products. Latex paints are widely used thermoplastic emulsion polymer latex paints.
5. The characteristics of latex paint
(1 ) Water is used as the dispersion medium, which is safe and low-pollution, generally only contains less than 5% co-solvent, and is low-toxic;
(2) Convenience in construction, it can be applied by rough coating, roller coating and spraying, and it is easy to clean the tools after construction; (3) The latex coating has good air permeability, can be applied on the surface of wet substrate, and is also very suitable for construction in hot and humid environment;
(4) The metal latex paint is diluted with water and has no fire hazard, so it is very suitable for the cross-operation of painting and welding in the shipbuilding industry;
(5) The paint dries quickly, allowing recoating within 0.5 ~ 2 hours, greatly shortening the construction period;
(6) The latex paint has a high solid content under the construction viscosity, and the coating film is thick at one time, which improves the construction efficiency;
(7) The relative molecular weight of the resin in the emulsion dispersion system is very high, the coating film has good weather resistance, and has good mechanical properties, alkali resistance and water resistance. As architectural coatings, it has good gloss and decoration; as metal latex coatings, it has general protective properties.
(8) The disadvantages of latex paint are poor film-forming properties at low temperatures, and generally need to be applied above 10°C; the paint is pseudo-plastic and easy to thicken, and the paint fluidity and wet film leveling are poor; the viscosity rises rapidly after water volatilization, and the film is easy to Bubbles and pinholes are produced; the surface tension of water is high, and the wettability of the coating to the substrate is poor. In the process of paint making and use, strong mechanical force will destroy the stability of latex paint, causing the paint to flocculate and deteriorate.
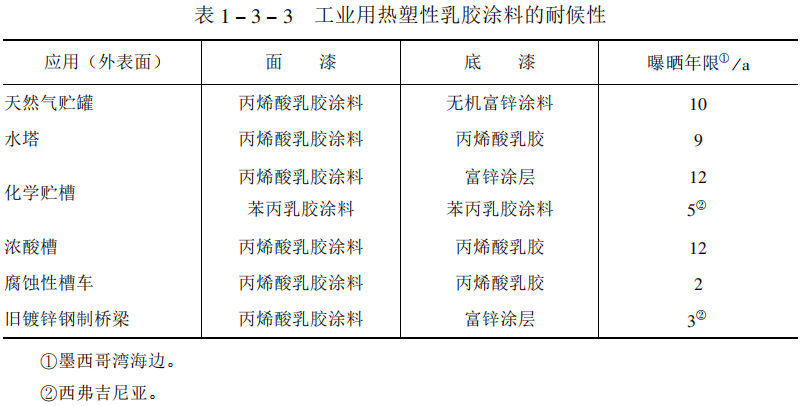
6. The durability of latex paint
Because the relative molecular weight of latex paint is very high, if both the primer and the top coat are made of latex paint, the durability will be more than 5 years when the total thickness of the coating is 100-150 μm, which is better than that of solvent-based paint. The weather resistance of industrial latex coatings is shown in Table 1-3-3.