Anti-drying shrinkage cracks (mud cracks) refers to the ability of the coating film to resist cracks caused by drying shrinkage. It refers to the cracks that appear during the drying process of the wet coating film, rather than the cracks that appear during the use of the film after drying.
1. Test method
Anti-drying shrinkage cracks are usually coated with a wedge gap applicator. For example, the gap of the wedge gap applicator is from 50 to 2000 μm and the width is 156mm. The wet film after coating is at (23±2)℃, RH= (50 ± 5)% of the standard conditions of curing 48h, and then observe at what thickness the dry film begins to crack. The dry film thickness at the beginning of cracking is the limit of the latex paint's anti-drying shrinkage crack, which is called anti-drying shrinkage crack, and the unit is μm , as shown in the figure.
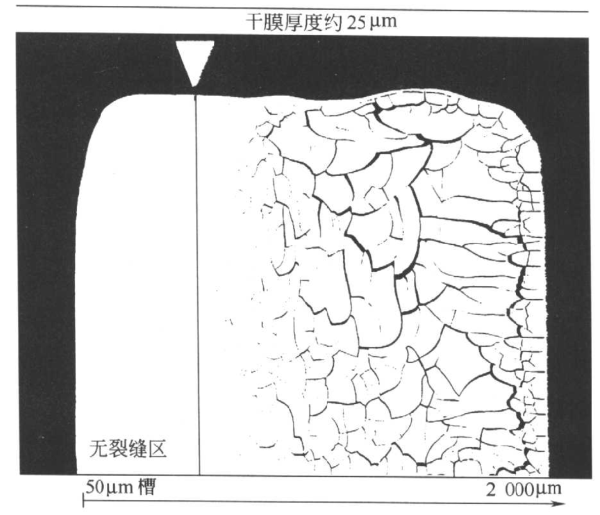
Measurement results of anti-drying shrinkage cracks
2. Requirements for anti-drying shrinkage cracks
For interior wall latex paint, the requirement for anti-drying shrinkage cracks is 400μm. For exterior wall latex paint, due to the poor flatness of the base layer, the requirement for anti-drying shrinkage cracks is increased to 900 μm . This is Germany's anti-drying shrinkage cracking requirement for latex paint.
Since the coating film applied in my country is generally thinner than that in Germany, and the texture is not strong, the requirements for anti-drying shrinkage cracks can be appropriately relaxed. But for the latex paint applied on the relief paint, the requirement of anti-drying shrinkage cracks must not be relaxed, but must be improved.






