The so-called process inks generally refer to three-color inks. In addition to fast drying and good printing performance, this type of ink is mainly required for the so-called purity, cleanliness, and overprinting performance of the color. The purity and cleanliness of the color is the main content of this type of ink. Use yellow, magenta (red) and blue to overprint secondary colors red, green and blue. If the overprint performance of yellow, magenta (red), and green oil poly is not good, it is impossible to obtain satisfactory red, green, and blue. If a set of color printing inks cannot produce more satisfactory colors , the application value of this set of color printing inks will be limited. Therefore, overprinting performance is also very important for color printing inks.
In this section, I want to focus on the color of the color printing ink, because the quality of the three colors of yellow, magenta (red) and cyan is the key to the quality of the printing printing ink.
From an optical point of view, the spectral colors in nature are the most desirable colors. If we can use the yellow, magenta (red) and cyan colors in the spectral colors to make color printing inks, that is the most satisfactory. But this is the color of light in nature. The distance between the color of the pigments we manufacture today and the spectral color is too large. Therefore, in fact, the color of all color printing inks is very different from the theoretical requirements.
Regarding some color characteristics of the color printing plate, here we will use the GATF color wheel diagram to illustrate.
We know that the color characteristics of a color printing plate have four aspects, namely 1. Intensity; 2. Hue; 3. Gray scale; 4. Efficiency. These four characteristics can be determined by calculation after measuring a color plate ink with three color filters with a reflection density meter (Reflectdensitometer).
Intensity: When comparing the intensity of different inks, the one with the highest value among the three color filters is the intensity of the ink.
The strength of the ink is very important because it determines the range and depth of the color. For example, the relative strength of yellow and cyan after overprinting will determine whether the resulting green is yellow-green or blue-green, and so on.
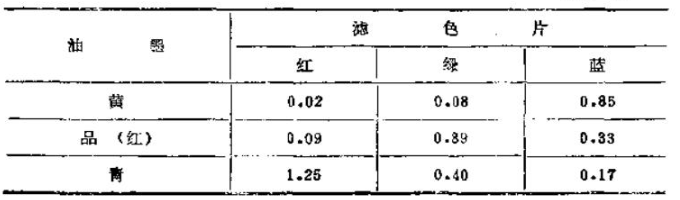
Hue and hue error (commonly known as color shift in the printing industry): The color of an object depends on its absorption and reflection of light and other factors. A satisfactory color printing ink should be able to absorb one-third and reflect two-thirds of the spectral color. For example, a satisfactory magenta should absorb all green and reflect all blue and red. A satisfactory yellow should be able to absorb all the blue and reflect the red and green of the whole county. A desirable cyan should absorb all red and reflect all green and blue, and so on.
The hue error of the color seal is due to the imbalance between its absorption and reflection. That is to say, one-third of what should be absorbed is not absorbed, and two-thirds should be reflected but two-thirds is not reflected. The hue error of the ink is expressed in a few percent, which can be calculated by the following formula:
Hue error = (medium-low)/(high-low) x100%
The high, medium and low shown in the formula refer to the data measured by three color filters. For example, in the table, the hue error of magenta (red) is:
(0.33-0.09)/( 0.89-0.09) x 100% = 0.24/0.80x100% = 30%.
Grayscale: The so-called purity of color printing ink is mainly determined by the grayscale multiplication. When the color printed on the paper reflects very little light (not bright light), the color becomes gray. For example, magenta should reflect red and blue completely, but because it reflects very little red, the gray scale is large. The gray scale is also expressed in a few percent, which can be calculated by the following formula:
grayscale = low/high x 100%
Take the magenta (red) in the table as an example, its grayscale is:
0.9/0.89x100%=10%
Efficiency: The so-called efficiency refers to whether a color really absorbs one-third and reflects two-thirds? If a color should reflect and not reflect, should absorb and not absorb, or even have the opposite effect, its efficiency will decrease. Therefore, the efficiency of a color can be obtained from the percentage of its correct absorption and incorrect absorption of light, which can be calculated by the following formula:
Efficiency=1-(low+medium)/2high x100%
If the teaching efficiency of a color is higher, when it is combined (printed) with other colors, a wider range of hues and relatively pure shades can be obtained.
Sometimes the efficiency of a color is the same, but the hue and grayscale may be different.
It can be seen that the so-called efficiency of each color ink is only useful for color printing inks, and it is meaningless for non-color printing printing inks.
With the above concepts, we can apply the CATF color wheel diagram. This kind of map can point out the hue error and gray scale of a color printing ink.
This kind of image is a clock dial (see figure), which is divided into 12 equal parts. Yellow Y is at the position equivalent to 2 point of the clock: magenta (red) M is at 6 point: green C is at 10 point; red R is composed of magenta (red) ) and yellow overprinted at 4 point; blue B - made of magenta (red) and cyan overprinted at 8 point; green G - made of cyan and yellow overprinted at 12 point; Each grid (including from inside to outside) is 10%. There are six areas of 0-100; that is, yellow Y-red R, red R-magenta (red) M; magenta (red) M-blue B, blue B-cyan C; cyan C-green G; green G- yellow Y.
According to the data in Table 1, after calculating with the above formula, the results in Table 2 can be obtained. The grayscale and hue error data in the table have been plotted in Figure 1. When determining the hue error coordinates of a color, the color filter with the smallest value will have a hue error.
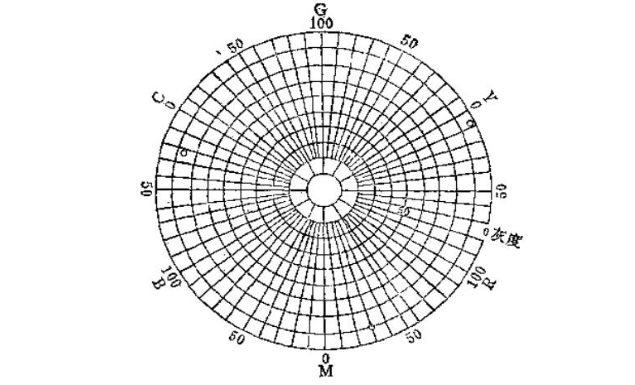
figure 1
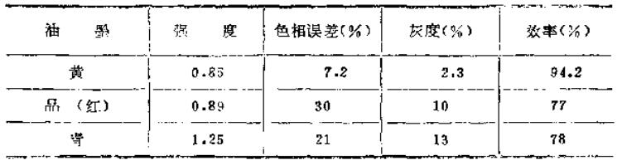
Table 2
Program the color of the color filter. For example, the hue error of yellow in Figure 2 is 7.2%. Since the smallest value is measured with a red filter, it should be 7.2% red when determining the coordinates. Gray coordinates are determined by outside-in calculations. If the grayscale coordinate position of a color is closer to the center, it means that the grayscale of the color is larger and the color is less clean.
According to the color wheel diagram, you can clearly see the hue error and grayscale of a color plate ink
The GATF color wheel diagram can be used to determine the situation of color plate inks on different papers. It can make people understand the limits and possibilities of a set of color plate inks, as well as overprint performance, ink opacity, light diffusion from the ink surface, etc. Generally speaking, the F color wheel diagram can achieve two purposes: 1. .Estimated secondary (secondary) color or tertiary (secondary) color overprint; 2. Compare with the correct (relatively speaking) color.
We know that when one kind of ink is overprinted on another ink, any hue between the two colors can be obtained, which depends on the relative strength, transparency and overprint performance of the two colors.
If yellow, magenta (red), cyan, and overprinted colors red, blue, and green are measured and calculated through a series of calculations, their coordinates are drawn (points) on the color wheel diagram, and then these points are connected by a straight line , then the area connected by this circle can basically explain the limit of this set of color printing ink and the pure color that can be produced. The larger the area connected by the circle, the higher the efficiency of this set of color printing ink.
Above, we have introduced some overviews of the GATF color wheel diagram and the relationship between the characteristics of the color printing ink. So for the overprint ink itself, is there any way to improve (change) their hue and cleanliness? Is there any way to control the cleanliness between their overprint colors? What about the internal relationship of these quality indicators? ?
As mentioned before , only spectral color has the most satisfactory color characteristics , but this is unattainable in the current actual situation , so the improvement of the color of the color printing ink can only be done when the actual conditions are possible. Work such as tint and cleanliness improvements on yellow, magenta, and cyan pigments to have the smallest hue error and smallest gray scale. But this work is always limited , people just want to do better under the guidance of theory.







