Printing has many influences on ink color, the first is color separation plate making, the second is printing speed, pressure and ink supply, of course, there are also ink drying and overprinting performance issues, and so on.
Color-separation plate-making technology can make an original with poor vividness be copied into a printed product with relatively bright vividness through color separation.
The faster the printing speed, the less the amount of ink that will be printed, and vice versa. Generally speaking, as the thickness of the ink layer increases, the brightness will decrease, but the saturation will increase accordingly, and the hue will tend to transmit light with a large coefficient. Therefore, the amount of ink (film) has an impact on the color. Figure 1 points out the spectroscopic curves when the amount of ink is different.
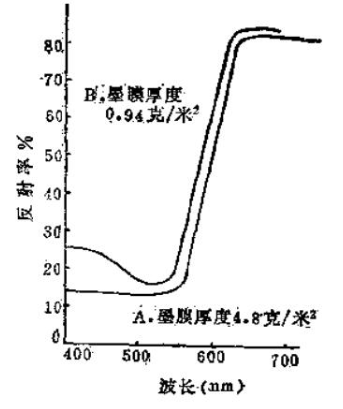
The thickness of the ink film and the balance of the overlapping amount of several colors will affect the color of the printed matter.
The ink drying problem is actually a problem of the amount of ink left on the paper. Of course, there is also the problem of color change after the ink dries. For a given paper, the faster the ink dries, the more ink is left on the paper. Obviously, the dryness of the ink is not only determined by the performance of the ink itself, but the printing worker can adjust it by adding a desiccant (oil).
The overprinting performance of ink (Ink Trapping) refers to the performance of a layer of ink printed on the paper first, which is no longer brought back to the printing plate by the next layer of ink transferred from the printing plate. The overprinting performance of the ink has a great influence on the printing result, and this point is sometimes not noticed by people.
In all color printing work, there are generally white ( paper), black, yellow, magenta (red ) , cyan, red, green, blue and other colors appearing. Whiteness depends on paper. Yellow, magenta ( red), and cyan depend on the color of the ink itself and the amount of ink to be controlled. Other colors such as red, green and blue depend largely on the overprint performance of the second, third or fourth printed ink. For example: Since the ink film formed by overprinting the magenta (red) ink on the yellow ink (an ink printed on the paper first) cannot be as thick as the ink film printed on the paper by the magenta (red) ink, it is desirable The red is impossible to form. The same is true for several other colors. In fact, the overprinting performance of the ink does not exist in all wet printing processes. Ink overprint performance also varies greatly, from about 30% to 90%, and the percentage in this case depends on the ratio of the thickness of the ink film overprinted on the previous ink to the thickness of the ink film printed on the paper. After a series of actual data measurements, it shows that in the four-color overprint, the highest overprint rate of magenta ink overprinted on yellow ink is about 78%, but the overprint percentage can vary from 50-95%.
If the overprinting properties of the ink are suitable and controllable, the resulting color can be expressed as:
Color=f(w)+f(y)+f(m)+f(c ) +f(k)
In the formula: w=whiteness of paper ;
y=yellow ink ;
m=magenta (red) color ink;
c=cyan ink ;
k = black ink.
Red, green, blue and black overprinted by three colors depend on the control of yellow and magenta (red) cyan inks.
If the overprint performance is poor, you will not get satisfactory red, green, blue and black colors.
In short, there are many factors that affect the color of ink. It depends on the raw materials (especially pigments) and the color matching ratio; it is related to paper and closely related to the printing process, etc.







