1 Fiber: Mechanical wood pulp and chemical wood pulp fiber paper are generally said to be relatively hard and less elastic, so it may cause paper rupture under embossing conditions (this is only a theoretical hypothesis). The slightly sized rag paper is relatively soft and absorbs ink.
2. Sizing: This makes the paper stiff and reduces its absorbency. Therefore, tissue paper with less sizing is relatively soft and absorbent, but the bonding between fibers is relatively loose, so it has the disadvantage of floating, and the printed dots are not clear. If the ink is slightly viscous, it is very easy to peel off .
3. Calendering: It can make the surface of the paper smooth and uniform in thickness, but the hardness of the paper will also increase accordingly. If you use medium pressure when printing, you can print better results. Supercalendered paper is not necessarily better, as it is harder and more solid, which tends to cause ink blots spread.
The smoothness of the paper has a considerable influence on the printing effect, because it will change the contact area of the ink layer and affect the transfer performance of the ink. For example, if the ink layer on the printing plate is very thin and the paper is very rough, the protruding part of the paper surface will be inked and the concave part will have no ink, resulting in insufficient ink coverage, that is, the so-called false imprint.
In this case, it is necessary to increase the amount of ink transfer so that the recessed part is also inked. This requires a thicker ink layer on the printing plate: and this is undesirable for high-quality prints. Therefore, increasing the film thickness on the printing plate seems to be a last resort to compensate for the rough surface of the paper. Of course, for paper with rough surface, it is also possible to increase the printing pressure to overcome the disadvantage of false ink imprinting.
4. Filling and coating: Filling can make the paper more uniform, because the filler can fill the gaps between fibers, which is beneficial to printing. Coated paper is relatively smooth and has moderate absorption performance. If you do not pay attention when printing, the disadvantage of ink spreading will also occur.
5. Porosity: The porosity of paper will affect the transfer performance and absorption performance of ink.
We know that the compression and elasticity of paper are closely related to its printing adaptability. Strong compressibility can make the loose structure inside the paper dense; because the paper has many pores, which can increase the ink absorption capacity, so the pressure penetration will increase with the increase of compressibility.
The elasticity of the paper refers to the percentage change of the thickness of the paper under the influence of the imprinting force. The elasticity of paper is also important for the transmission of oil. Especially in gravure printing, the characteristic of gravure ink transfer is that the ink surface in the mesh hole presents a meniscus shape. The ink surface and paper can only come into contact through local deformation of the paper surface.
In the multi-color printing process, only when the paper has enough elasticity and can repeat such deformation can better printing effect be obtained.
The bulkiness of paper can be measured by air permeability. Table 20-3 illustrates the porosity of three different papers, which is the time (in seconds) required to pass through 100 cm³ of air. Generally speaking, loose paper absorbs better.

6. Penetration of paper - absorption (ink) property: this item is very important for the fixation of ink. As can be seen from the above table, the air permeability of newsprint is faster, and it can be considered that it has better porosity. Cellophane is airtight.
Under the general concept, loose paper has better absorption, and it is proportional to the thickness and viscosity of the inhaled medium (linking material), that is, the smaller and thinner the viscosity of the medium, the faster it will penetrate into the paper.
7. Dryness of paper and ink: Generally speaking, paper with good absorbency dries faster, while paper with hard and poor absorbency dries slowly. Acidic paper dries slower. Coated paper dries faster. For non-coated paper, when the pH value is lower than 4.8, it will obviously affect the dryness of the ink. Generally, when the humidity is relatively low, the drying rate of different types of non-coated papers is not much different, but when the humidity is relatively high, the dryness of super calendered paper is much higher, and this is the case for offset paper.
The alkalinity of coated paper is beneficial to the drying of ink. This can be seen , which shows the effect of different pH values on the coated paper surface on the dryness of a black offset ink at different relative humidity conditions.
The acid in the paper is harmful to the dryness of the ink, because the acid can react with the metal in the desiccant to form a non-oil-soluble product, which is especially serious in the case of high humidity It is generally believed that the wet paper fiber can remove the desiccant from the ink.
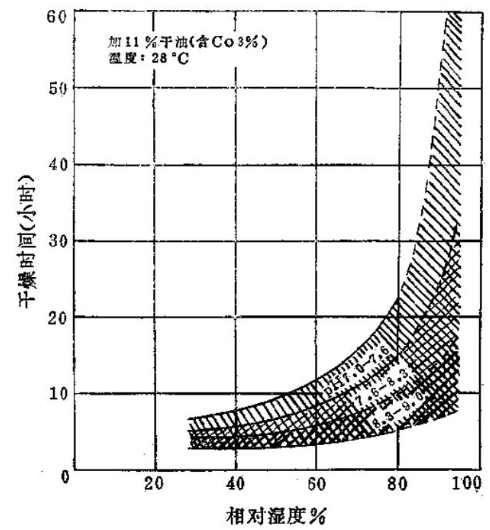
Figure 1 Effect of PH value of paper coating on ink dryness






