(1) Experimental principle
The test principle of the pressure difference method is shown in Figure 3-4. The gas flows from the high pressure side through the side of the barrier material to the low pressure side, creating a vacuum or negative pressure on one side of the plastic film, causing a pressure difference on both sides of the film, and measuring It is the change in pressure differential across the barrier material. The differential pressure method can accurately measure the amount of trace gas passing through a plastic film with low gas permeability in a short time.

Figure 3-4 Principle of differential pressure method
1-inlet ; 2-outlet ; 3-sample ; 4-soft rubber ring; 5-glass disc ; 6-mercury ; 7-capillary
The volume of the plenum chamber on the low pressure side should be kept constant and the rate of pressure increase measured. Using this principle, a glass pressure measuring tube is sealed into the bottom plate of the air-permeable chamber with epoxy glue, and a sintered glass plate is placed on the concave surface of the bottom plate to form a general flat joint surface. After the glass plate is covered with the sample , and then put a soft rubber ring to make the air chamber completely sealed. After evacuating the air-permeable chamber, inject the measured gas, and when the pressure of the manometer is stable at an appropriate value (should be controlled within the range of 6.67-13.33Pa), tilt the instrument to allow mercury to flow into the capillary and U-shaped tube from the reservoir. , and then return the instrument to the vertical position. As the gas permeates the sample, the pressure rises, and this value is represented by the mercury surface drop height of the capillary, as shown in Figure 3-5.

Figure 3-5 Determining the falling height of the mercury column for oxygen transmission rate
(2) L100-4200 film air permeability Tester
L100-4200 film air permeability Tester is suitable for measuring the air permeability of plastic film, composite film, leather and other materials. Maintain an air pressure of 13.33Pa on one side of the film, and form a vacuum (negative pressure) on the other side. Under the action of the pressure difference in the instrument, the test gas penetrates from the side with high pressure to the side with low pressure. The measurement results Expressed in mL/(m2·24h).
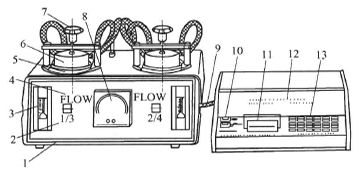
Figure 3-6 L100-4200 Film Air Permeability Tester
1-frame; 2-panel; 3-rotameter; 4,6-measurement chamber; 5-sample; 7-sample clamping; 8-vacuum gauge; 9-cable; 10-printing paper control; 11 - printer; 12 - monitor; 13 - keyboard
①Structure and working principle The L100-4200 film air permeability Tester is composed of a microprocessor-controlled memory storage unit, a measurement chamber, a water circulation cooling constant temperature box, a two-stage Vacuum Pump and a gas supply system with a decompression device, as shown in Figure 3-6 shown. The test gas enters the upper measurement chamber, the air pressure is controlled by the pressure reducing valve, the flow rate is indicated by the flow meter, the sample is clamped between the upper and lower measurement chambers, the lower measurement chamber is connected with the vacuum gauge, and the negative pressure is generated by the Vacuum Pump. The degree of vacuum is indicated by a vacuum gauge. Except that the air inlet pipe is set in the upper measuring chamber, other pipe joints are installed on the rear panel of the host.
Figure 3-7 is the pipeline diagram of the L100-4200 film air permeability Tester, which is developed by Switzerland LYSSY company. All the testing procedures are solidified in the computer storage, the whole testing process is controlled by the computer, and the test results are automatically printed out .

Figure 3-7 L100-4200 type film air permeability Tester pipeline
②Main technical parameters
a. Measuring range: 1~10.000mL/(m2-24h).
b. System sensitivity: 0.02mL/(m2·24h).
c. The minimum response of the Detector: 0.02mL/(m2- 24h).
d. Sample size: 100mm×100mm.
e. Sample thickness: 0.01~2mm.
③ Calibration procedure
a. Install the instrument, connect the water cooling circulation system, connect the Vacuum Pump and the gas supply system.
b. Clear the residual gas in the measurement chamber. After the instrument is installed, a layer of grease should be lightly applied to the upper and lower sealing surfaces, and the aluminum foil should be placed in the middle of the measuring room. Temperature adjustment.
c. Properly select the pressure interval. Since various sealing links of the measurement system have penetration, the microcomputer measurement system will automatically adjust. If the pressure interval between 650 and 750Pa is selected, it is easy to remove residual gas to reduce the impact on the measured value.
d. Select a thermoplastic standard sample with known permeability—polyester film. When the selected pressure is 0-13.33Pa, the response characteristics of the vacuum gauge do not depend on the thermal conductivity of the gas. Therefore, it is possible to calibrate an instrument with one gas and obtain a fixed set of parameters that can be used to measure other gases. These fixed parameters are printed and brought to the user with the instrument.
In addition, the BTY-Bl gas permeability Tester is suitable for testing the gas permeability and barrier properties of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and other materials such as plastic films and composite films. It adopts heat insulation and moisture insulation technology to make the test conditions more stable and consistent, and is fully automatic controlled by computer, so the test is effective and accurate. Its main technical parameters are as follows.
a . Measuring range: 1 ~ 10000cm3/ (m2 - 24h-0.1MPa).
b. Resolution: 0.01Pa.
c . Operating temperature: 0~50°C (standard 23°C).
d. Sample size: $86mm.
e. Through area: 38.48cm2.
f. Number of samples: 1, 2, 3.
g. Test gas: O2, N2, CO2 and other dry gases with a purity of 99.9%.
In addition, the main technical parameters of VAC-V2 differential pressure gas permeatIon Meter are as follows.
a. Test range: 0.05~50000cm3/(m2·24h·0.1MPa) (conventional); the upper limit is not less than 500000cm3/(m2·24h·0.1MPa) (extended volume).
b. Temperature control range : 5~95°C, precision ±0.1°C.
c. Humidity control range : RH 0, RH 2%~98.5%, RH 100%, accuracy RH±1%.
d. Vacuum degree of Test Chamber : <20Pa.
e. Sample size : 97mm.
f. Number of samples : 3 pieces (data are independent).
g. Permeable area : 38.48cm2.
h. Test gas : O2, N2, CO2 and other gases.
(3) Test method
The test was carried out in accordance with the national standard GB 1038 "Plastic Film Air Permeability Test Method". The whole test process is carried out under the required constant temperature conditions. The specific test steps are as follows.
① Measure the thickness of the sample according to the national standard GB 6672. For each group of 3 samples, select at least 5 measurement points and take the arithmetic mean value.
②Put a circular sample with a diameter of 75mm on a coarse filter paper with a diameter of 66mm, and seal it in a ventilating chamber, connect the ventilating chamber with the main pipe with a rubber tube, and seal the joint with vacuum sealant. At this point, all the mercury in the vent chamber manometer is in the reservoir.
③Close the high-pressure side piston of the ventilation chamber to vacuumize. Use a high-frequency vacuum leak Detector to detect the high-voltage side, and check whether there is any air leakage in the film sample . After confirming that the film sample has no pinholes and no air leakage, open the high-pressure side piston and continue to evacuate to the specified vacuum degree (should be controlled within the range of 13.33~1.333Pa). Pour the mercury in the reservoir into the pressure gauge in the gas chamber.
④Input the dry gas into the gas cylinder to the specified pressure, open the high-pressure side piston of the ventilation chamber, and immediately record the mercury column height (read to 0.5mmHg) and the pressure of the high-pressure side (read to 1mmHg) in the pressure gauge of the ventilation chamber . Afterwards, record the mercury column height of the manometer in the ventilating chamber at regular intervals. After reaching a stable penetration, continue to record three times and take the arithmetic mean value. It should be noted that the selection of the time interval should be based on the drop of the mercury column height by 5mm in the gas chamber manometer. The difference in the height of each drop of the mercury column of the pressure gauge in the breathable chamber does not exceed 10%, which can be considered as stable penetration.
⑤ After the test, remove the vent chamber, pour all the mercury in the pressure gauge in the vent chamber back into the container, take out the sample, and prepare for the next test.
⑥Calculate the gas permeation rate and air permeability coefficient.
At a certain temperature, a certain gas pressure difference is maintained on both sides of the sample, and the calculation method of the gas permeability coefficient (P) and gas permeability (Q ) is:

In the formula, Pg——air permeability coefficient, cm3 cm/( cm2 s Pa);
Qg——air permeability, cm3 /(m2·24h · Pa);
Δp/ Δt —Arithmetic mean value of the air pressure change on the low pressure side per unit time at stable penetration, Pa/s;
V——low pressure side volume, cm3;
A - the test area of the sample, cm2 or m2;
l—thickness of sample, cm;
T - test temperature, K;
T0——the temperature under the standard state, 273.15K;
P0——gas pressure under standard state, 1.0133×105Pa;
P1-P2—the pressure difference on both sides of the sample, Pa.
The test results are expressed as the arithmetic mean of each group of samples, with at least two significant figures.
For example, according to the national standard GB 1038 "Plastic Film Gas Permeability Test Method", the BTY-B1 gas permeability Tester (pressure difference method) was used to test and analyze the oxygen and carbon dioxide of 12μm PET, 20μm PET film and 18μm PET aluminized film under different temperature conditions. Air permeability, air permeability versus temperature curve (Figure 3-8) shows that the air permeability of PET film and PET aluminized film to H2O, O2 and CO2 increases with the increase of temperature, and PET film has a certain resistance to oxygen and carbon dioxide. Significant selective permeability, the CO2 air permeability of 12μm and 20μm PET films is significantly higher than the О2 air permeability, and the CO2 air permeability is about 2 times that of the О2 air permeability. PET aluminized film has low permeability to O2 and CO2 gases, and has excellent barrier properties, but it has no significant selective permeability to oxygen and carbon dioxide gases.

Figure 3-8 The gas permeability-temperature change curve of PET film
(4) Factors affecting air permeability coefficient
① pressure
For O2, CO2, Ng, Hg and other gases, the air permeability coefficient has nothing to do with pressure. When polyethylene film and polyvinyl chloride film are tested for N, the pressure difference on both sides of the film has little effect on the air permeability coefficient and air flow rate.
②The type and nature of the diffused gas, the larger the diameter of the gas molecule is, the larger the required diffusion activation energy is, and the smaller the diffusion coefficient is for the permeation of the same plastic film. But when the critical temperature of the gas is quite large, the gas permeability coefficient mainly depends on the solubility coefficient.
③Film properties










