This test is suitable for evaluating the load-carrying capacity of large transport packages during loading, unloading and lifting, as well as the protection capacity of the package for the contents . The speed of operation during hoisting and the speed of emergency starting and braking have a great influence on the increase of extrusion force on the rope and the package. In the normal emergency braking process, the increment of the force of the wire rope on the packing box is generally in the range of 30% to 50%. Due to the extrusion force of the lifting rope on the packing box, the packing box will be deformed or even damaged.
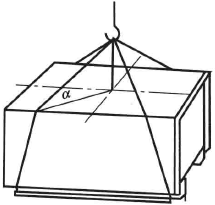
Figure 6-25 Lifting test principle
The principle of the lifting test is to place the steel wire rope at the predetermined lifting position of the package skid, and lift, brake and land the package according to the predetermined lifting speed, lifting method and number of times. Figure 6-25 is the lifting test principle. The specific test method is that the angle between the steel wire rope and the top surface of the package is within the range of 45°~50°, and the package is lifted to a certain height (about 100~150cm) by a lifting device at a normal speed , and then the emergency The way of lifting and braking is to repeatedly rise, fall and run left and right for 3-5 minutes, and then fall to the ground at a normal speed, and repeat the test 3-5 times.
The record of the lifting test results is mainly to measure the diagonal deformation of the end face and side of the package and the deflection of the sliding wood before and after each lifting. The measurement of skid deflection after lifting shall be carried out before the package falls to the ground. In addition, other damages to the package should be checked and recorded.
