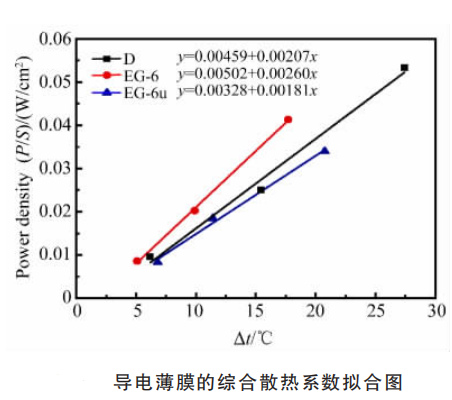
In this paper, two different exfoliated graphene EG-6 and EG-6u were prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide exfoliation method, and conductive films with graphite D and exfoliated graphene EG-6 and EG-6u as conductive fillers were prepared. The morphology, size and three kinds of conductive films of the raw material graphite were characterized by scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy. The electrothermal characteristics of the prepared film were tested, and the resistivity of the material and the heating characteristics such as heating rate, heating time, and comprehensive heat dissipation coefficient during the heating process and in a stable working state were compared.
Preparation of conductive coating and conductive film
Take 20g of natural flake graphite (500 mesh), 3g of dispersant DS-192, 0.3g of dispersant 701, 100mL of pure water, and stir for 30min at a stirring speed of 800r/min to prepare graphite conductive coating D, and then uniformly dispersed graphite Put it into a high-pressure reactor, heat the reactor and fill it with CO2 gas, so that the temperature and pressure reach 45°C and 6MPa respectively. After keeping for 150 minutes, it was collected to obtain the exfoliated graphene conductive coating EG-6; then ultrasonicated at 2000 Hz for 120 minutes to obtain the exfoliated graphene conductive coating EG-6u. Use a heating type film coating machine to coat the non-woven fabric substrate, cut it into a conductive film with a size of 12mm×10mm after natural drying for 48 hours, and stick a 10mm wide conductive copper tape on both ends for testing. The conductive films are respectively marked as D. EG-6, EG-6u.