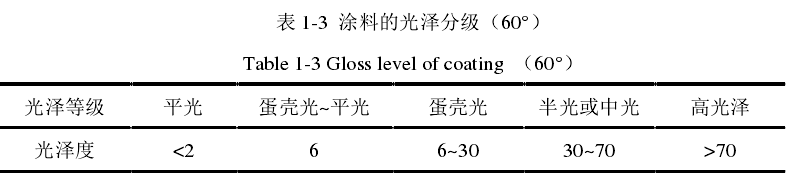
According to the definition of gloss in the international general standard, a fixed oblique angle is usually used to measure the gloss of the surface. The testing principle of the gloss meter is shown in Figure 1-6155. The fixed light source G emits a beam of parallel light with an incident angle of ε1 through the lens L1 . The parallel light is reflected and scattered by the surface of the object. The reflection angle ε2-81 The light is collected at the optical signal receiver B through the lens L2 , and the photoelectric signal is processed and the measurement result is displayed on the instrument.
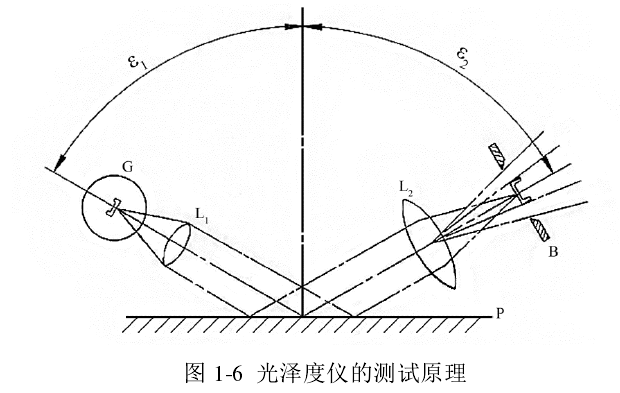
In the measurement of the gloss meter, the black glass with a refractive index n D = 1.567 is used as the reference standard, assuming that the glass plane is satisfactorily polished, it mirrors the light emitted by the light source, and defines the gloss of the plane at this time The degree is 100. The glossiness of the plane to be tested is shown in formula 1-1
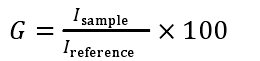
Among them, I sample is the intensity of the reflected light of the plane to be measured, and Lefere is the intensity of the reflected light of the reference plane. It should be pointed out that the measured gloss is also different when the incident angle is different. Commonly used incident angles are 20°, 45°, 60°, 75° and 85°, and 60° is generally selected. According to the measurement results of the 60° angle gloss, the paint can be divided into different grades, as shown in Table 1-3 541. In order to improve the accuracy of measurement, different gloss boards are used as reference planes when measuring paints with different . The high gloss reference board is made of black glass, and the medium gloss and low gloss reference boards are made of glazed ceramic or Made of frosted black glass.