Polyurethane coatings can be divided into two-component and one-component. Today we are going to introduce the testing requirements for two-component solvent-based polyurethane coatings under the HG/T 2454-2014 standard. Before the introduction, we need to understand that solvent-based polyurethane coatings are divided into two types according to the main application areas.
Type I products are solvent-based polyurethane coatings for concrete surfaces, which are divided into categories 1 and 2 according to coating properties. They are suitable for concrete facilities such as storage tanks and bridges; General-purpose primers and intermediate paints, interior topcoats, and exterior topcoats, among which exterior topcoats are classified into Class 1 and Class 2 according to the coating performance. Type II products are suitable for interior decoration and protection of steel structures, metal furniture, hardware products and other surfaces, and exterior surface coatings are suitable for decoration and protection of outdoor steel structures.
Item detection
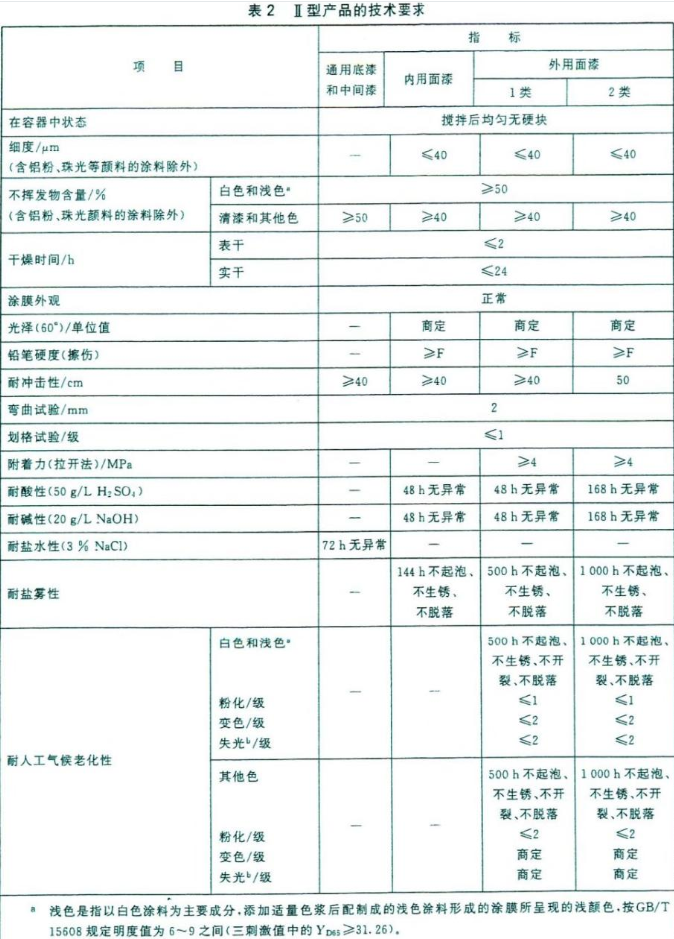
Performance requirements of Type I products
1. The state in the container: if the samples of type 1 and type 2 are stirred without hard lumps and are in a uniform state, they are regarded as up to standard.
2. Fineness: If the test results of Type 1 samples and Type 2 samples show that the fineness value is ≤ 40 μm, it is regarded as up to standard. (Note: Except for paints containing aluminum powder, pearlescent and other pigments)
3. Non-volatile matter content (Note: Except for paints containing aluminum powder, pearlescent and other pigments)
a. White and light-colored pigments are used for testing. If the test results show that the non-volatile content of both type 1 samples and type 2 samples is ≥50%, it is considered to be up to standard.
b. Use varnish and other colors to test. If the test results show that the non-volatile content of both type 1 samples and type 2 samples is ≥ 40%, it is considered to meet the standard.
4. Drying time: If the surface-drying time of type 1 samples and type 2 samples is ≦2h, and the hard-drying time is ≦24h, it is considered to be up to standard.
5. Appearance of smearing: use visual inspection method, if the observation result of type 1 sample and type 2 sample is that the coating film is uniform without sagging or other coating film pathology, it can be rated as "normal".
6. Gloss: The gloss standards of Type 1 samples and Type 2 samples are determined by the testing parties according to the actual needs of the product.
7. Impact resistance: If the test result of type 1 sample is ≥ 40cm, and the test result of type 2 sample is ≥ 50cm, it is regarded as up to standard .
8. Bending test: If the bending index of Type 1 samples and Type 2 samples is 2mm, it is regarded as up to standard.
9. Adhesion: We use the pull-off method to test the sample with a test column with a diameter of 20mm. If the observation results of class 1 samples and class 2 samples are both ≥3MPa, it is regarded as up to standard.
10. Acid resistance: immerse type 1 samples in 50g/L H₂SO₄ solution for 48 hours, immerse type 2 samples in 50g/L H₂SO₄ solution for 168 hours, take them out and wipe them dry and observe, if type 1 samples and type 2 samples If two of the three test panels do not show any pathological phenomena of coating film such as blistering, cracking, and peeling, they can be rated as "no abnormality"
11. Alkali resistance: immerse type 1 samples in saturated Ca(OH)₂ solution for 96 hours, immerse type 2 samples in saturated Ca(OH)₂ solution for 240 hours, take them out and dry them, and observe them visually, if If two of the three test panels of class 1 samples and class 2 samples do not show any pathological phenomena of coating film such as blistering, cracking, and peeling, it can be rated as "no abnormality"
12. Water resistance: Immerse Type 1 samples in the aqueous solution for 96 hours, and immerse Type 2 samples in the aqueous solution for 168 hours. After taking them out and drying them, observe them visually. , it can be rated as "no abnormality"
13. Resistance to artificial weathering:
a. Soak Type 1 samples in white paint and light-color paint for 500 hours, and immerse Type 2 samples in white paint and light-color paint for 1000 hours. After taking it out and wiping it dry, observe it by visual inspection. If the test results show that there are no blistering, cracking, peeling off, etc. of the coating film in the samples of type 1 and type 2, and the chalking≦1 grade, discoloration≦2 grade, and gloss loss≦2 level, the standard is met.
b. Dip type 1 samples in other color coatings for 500h, and type 2 samples in other color coatings for 1000h. After taking it out and wiping it dry, observe it by visual inspection. If the test results show that there are no blistering, cracking, and peeling off of the coating film in the type 1 sample and the type 2 sample, and the pulverization is less than or equal to level 1, the discoloration and loss of light shall be agreed upon by the testing parties. It is considered qualified.
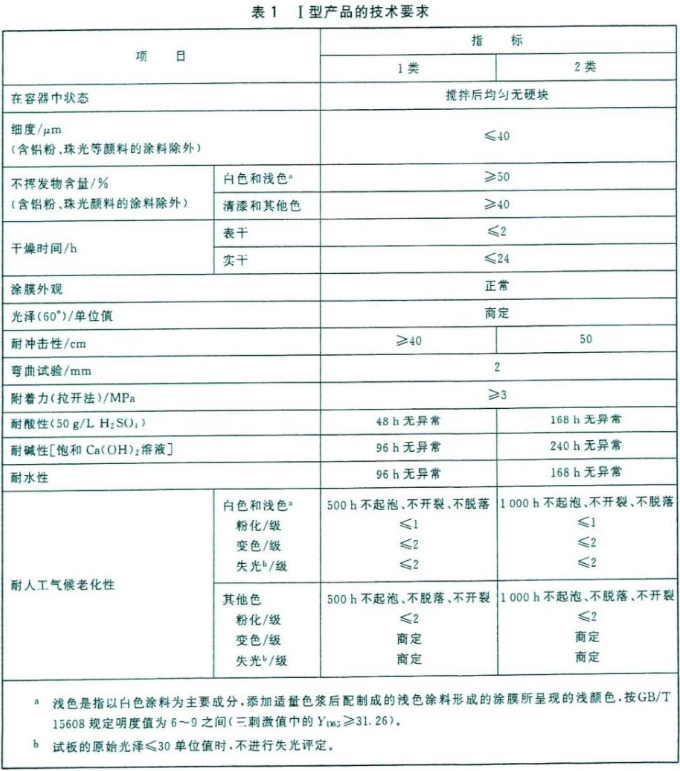
Performance requirements for Type II products
1. The state in the container: if the general primer and intermediate paint, interior topcoat, and exterior paint have no hard lumps after stirring, and are in a uniform state, it is considered to be up to the standard.
2. Fineness: If the test results of the intermediate paint, interior topcoat and exterior paint are fineness value ≤ 40μm, it is regarded as up to standard. (Note: Except for paints containing aluminum powder, pearlescent and other pigments)
3. Non-volatile matter content (Note: Except for paints containing aluminum powder, pearlescent and other pigments)
a. White and light-colored pigments are used for testing. If the test results show that the non-volatile content of general-purpose primers and intermediate paints, interior topcoats, and exterior paints are all ≥ 50%, it is considered up to the standard.
b. Use varnish and other colors for testing. If the test results show that the non-volatile content of general-purpose primers and intermediate paints is ≥50%, and the non-volatile content of interior topcoats and exterior paints is ≥40%, it is considered to meet the standard.
4. Drying time: If the surface-drying time of general-purpose primer and intermediate paint, interior topcoat, and exterior paint is ≦2h, and the hard-drying time≦24h, it is considered to meet the standard.
5. Appearance of smearing: use visual inspection method, if the observation results of general-purpose primer and intermediate paint, internal topcoat, and exterior paint show that the coating film is uniform without sagging and other coating film abnormalities, it can be rated as "normal".
6. Gloss: The gloss standard of interior topcoat and exterior paint is determined by the testing parties according to the actual needs of the product.
7. Pencil hardness: If the pencil hardness of interior topcoat and exterior paint is ≥ F, it is regarded as up to standard.
8. Impact resistance: If the test result of general primer and intermediate paint, interior topcoat, and exterior paint is ≥ 40cm, and the test result of category 2 of exterior paint is ≥ 50cm, it is considered to meet the standard.
9. Bending test: If the bending index of the general primer and intermediate paint, interior topcoat and exterior paint is 2mm, it is regarded as up to standard.
10. Adhesion: We use the pull-off method to test the sample with a test column with a diameter of 20mm. If the observation results of exterior paints 1 and 2 are both ≥ 4MPa, it is regarded as up to standard.
11. Acid resistance: Immerse the internal topcoat and exterior paint Type 1 in 50g/L H₂SO₄ solution for 48 hours, and immerse the Type 2 exterior paint sample in 50g/L H₂SO₄ solution for 168 hours, take it out and wipe it dry and observe. If two of the three test panels for interior topcoat and exterior paint 1 and 2 do not show any pathological phenomena of coating film such as blistering, cracking, and peeling, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
12. Alkali resistance: immerse the internal topcoat and exterior paint 1 in 20g/L NaOH solution for 48 hours, and immerse the exterior paint 2 samples in 20g/L NaOH solution for 168 hours, take it out and dry it, and observe it visually , if two of the three test panels of the type 1 sample and the type 2 sample do not have any pathological phenomena such as blistering, cracking, and peeling of the coating film, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
13. Salt water resistance: soak the general primer and intermediate paint in 3% NaCl solution for 72 hours, take it out and wipe it dry, and observe it visually. If there is no abnormal phenomenon of coating film such as blistering, cracking, peeling, etc., it can be evaluated to "no exception".
14. Salt spray resistance: immerse the interior topcoat in the solution for 144 hours, the exterior paint type 1 in the solution for 500 hours, and the exterior paint type 2 in the solution for 1000 hours. After taking it out and drying it, observe it visually. If the paint film has pathological phenomena such as rusting and peeling off, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
15. Cold resistance and weather aging:
a. Soak Type 1 exterior paint in white paint and light-color paint for 500 hours, and soak Class 2 exterior paint in white paint and light-color paint for 1000 hours. After taking it out and wiping it dry, observe it by visual inspection. If there is no rust, cracking, peeling and other pathological phenomena of the coating film, and the chalking≦1 grade, discoloration≦2 grade, and gloss loss≦2 grade, it is regarded as up to standard.
b. Soak Type 1 exterior paint in other color coatings for 500h, and soak Type 2 exterior paint in other color coatings for 1000h. After taking it out and wiping it dry, observe it by visual inspection. If the test result shows that there is no rust, cracking, peeling and other pathological phenomena of the coating film, and the pulverization is less than or equal to level 1, and the discoloration and loss of light are agreed upon by both parties, it is considered to meet the standard.