Waterborne wood coatings have the characteristics of low hazard and low pollution, and are widely welcomed in the home decoration and furniture coating market. Today we will introduce the provisions of GB/T 23999-2009 on water-based wood coatings. We need to understand its classification before testing.
Water-based wood coatings are divided into four categories: A, B, C, and D according to their actual use and function. Class A is the top coat for flooring, which is used for all wooden floors such as factory coating and home coating; Class B is the top coat for furniture, which is the top coat for factory coating wooden furniture; Class C is the top coat for decoration. It is a finish paint for wooden surfaces except Class A and B, mainly used for coating door covers, window covers, wall panels, etc.; Class D is primer and intermediate paint, which can be matched with all kinds of top coats. The wood used is painted with a primer.
Item detection
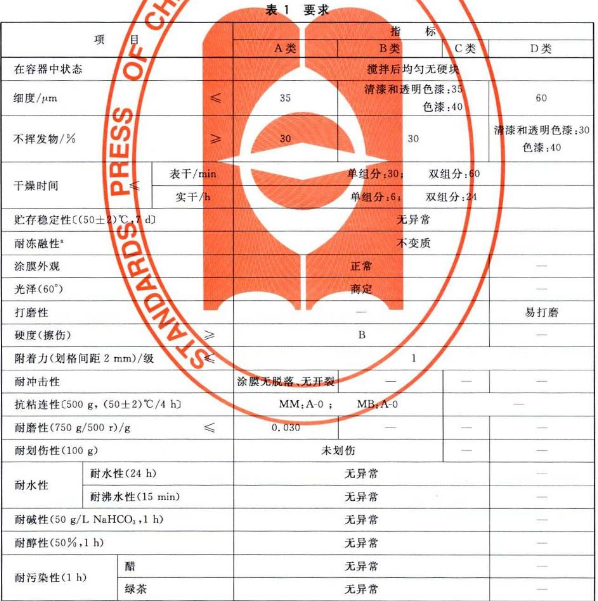
1. State in the container: First, we open the container, stir with a spatula or stir bar, and allow precipitation at the bottom of the container. If the primer sample, intermediate paint sample and top coat sample are easy to mix uniformly after stirring, it is rated as "homogeneous and no hard lumps after stirring".
2. Fineness: If the sample of type A is ≤35μm; the varnish and transparent color paste of the type BC sample is ≤35μm, the color paint is ≤40μm; the type D is ≤60μm, it is regarded as up to the standard.
3. Non-volatile matter content: if the sample of type A is ≥30%; the varnish and transparent color paste of the type BC sample is ≥35%, and the color paint is ≥40%; the type D is ≥60%, it is regarded as up to standard.
4. Drying time: If the surface-dried one-component ≤ 30h, two-component ≤ 60h, hard-dried single-component ≤ 6h, two-component ≤ 24h, it can be considered up to the standard.
5. Storage stability: put the sample in a constant temperature Drying Oven at 50 ℃ ± 2 ℃, take it out after 7 days, and observe it after placing it at 23 ℃ ± 2 ℃ for 3 hours. If it is uniform without hard lumps after stirring, it will be rated as "passed" .
6. Freeze-thaw stability: If the observation result is no deterioration, it is regarded as up to standard.
7. Appearance of the paint film: If the ABC sample has no wrinkles, stains, particles, shrinkage cavities and uneven gloss, it can be rated as "normal".
8. Gloss: 60° is used, and the parameters are determined by the testing parties according to the actual situation.
9. Grinding property: Class D products need to be "easy to grind" to meet the standard.
10. Hardness: The hardness level of ABC samples must be ≥ B to meet the standard.
11. Adhesion: The distance between the scratches is 2mm. If the sample parameters are ≤ grade 1, it is considered up to the standard.
12. Impact resistance: If the test result of the A-type sample is "no shedding or cracking of the coating film", it is considered to be up to the standard.
13. Anti-adhesion property: place the AB type sample in an environment of 50 ℃ ± 2 ℃ for 4 hours, if the test result is MM: A-0; MB: A-0, it is regarded as up to standard.
14. Abrasion resistance: under the detection requirement of 700g/500r, if the sample of type A is ≤0.030g, it is regarded as up to the standard.
15. Scratch resistance: Under the test requirement of 100g, if the test result of the AB sample is "no scratch", it is regarded as up to the standard.
16. Water resistance
a. Water resistance: If the ABC sample is immersed in water for 24 hours, and then visually observed under scattered light after the end, if there is no abnormality of the coating film, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
b. Boiling water resistance: If the ABC sample is immersed in boiling water for 15 minutes, and then visually observed under scattered light, if there is no abnormality in the coating film, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
17. Alkali resistance: If the ABC sample is immersed in 50g/L NaHCO3 for 1 hour, and then visually observed under scattered light after the end, if there is no abnormality of the coating film, it can be rated as "no change".
18. Alcohol resistance: If the ABC sample is immersed in 50% alcohol for 1 hour, and then visually observed under scattered light after the end, if there is no abnormality in the coating film, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
19. Pollution resistance
a. If the ABC sample is soaked in vinegar for 1 hour, and visually observed under scattered light after the end, if there is no abnormality of the coating film, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
b. If the ABC sample is soaked in green tea for 1 hour, and visually observed under scattered light after the end, if there is no abnormality in the coating film, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
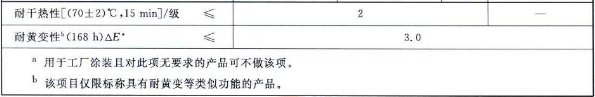
20. Dry heat resistance: place the ABC sample in an environment of 70 ℃ ± 2 ℃ for 15 minutes. If the test result is that the ABC sample is ≤ grade 2, it is regarded as up to standard.
21. Anti-yellowing property: place the ABC sample for 168 hours, if △E≤3.0, it is regarded as up to standard.