Minimum film forming temperature
Defined in various ways, but broadly speaking, it marks the beginning of small-scale movements in polymers. It is heavily influenced by the chemical structure, especially by the bulk of the side groups (steric hindrance).
The molecular weight dependence of the glass transition is fairly simple and is given by:
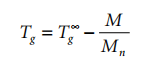
where is the limiting value of Tg at high molecular weight.
The effect of plasticizers on Tg has been well documented. According to Bueche's theoretical treatment11, the reduction of Tg by plasticizer can be calculated by the following formula
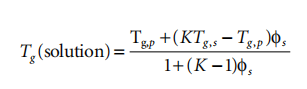
where Tg,p and Tg,s are the glass transition temperatures of polymer and solvent, respectively, and φs is the volume fraction of solvent. Then we write
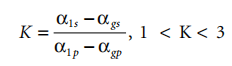
where αl = coefficient of volume expansion above Tg, αg = coefficient of volume expansion below Tg.
To calculate the Tg of a solution, the Tg of the solvent should be known 12 or estimated as 2Tm/3, and K is usually 2.5.
tension and shear
In the case of viscoelastic polymers, both tensile modulus and shear force are functions of temperature and time. We will limit our discussion to the temperature dependence of the isochronous modulus.
(Because tensile modulus and shear modulus are related by using an equation involving Poisson's ratio, the comments here on shear modulus G can also be extended to tensile modulus E.)
For semi-crystalline polymers below Tg, the modulus can be estimated as
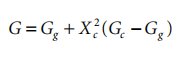
where Gg and Gc are the moduli of fully amorphous and fully crystalline polymers, respectively, and Xc is the degree of crystallinity.
Above Tg, the same equation can be used, but with Gc far exceeding Gg, Equation 4.9 simplifies to
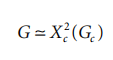
For amorphous polymers above Tg, the modulus is given by the rubber-elastic expression:
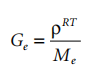
where is the entanglement molecular weight (see Section 4.2.1.2). This rubbery platform of uncrosslinked polymers is only observed at molecular weights above zero.
For crosslinked amorphous polymers (elastomers) above Tg, the modulus is given in a similar way:
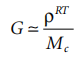
where Mc is the molecular weight between permanent crosslinks. The trapped entanglement also plays a role in determining the modulus when Mc exceeds Me:
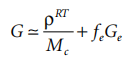
where Ge is given by Equation 4.11 and fe is the probability factor for capturing entanglement.








