The following discussion of accelerated aging light sources is limited to UV spectral issues. It does not address issues such as photostability, effects of moisture and humidity, effects of cycling, or reproducibility of results. For simulations of direct sunlight, artificial light sources should be compared to what we call "solar maximum" conditions: global, midday sunlight, summer solstice, normal incidence. Solar maximum is the most severe condition encountered in outdoor service and, as such, controls which materials fail. Comparing light sources to "average better sunlight" is misleading, which is simply the average of the less damaging March 21st and September 21st equinox readings. In this chapter, charts labeled "Sunny" refer to solar maximum: noon, global, midsummer sunshine. Despite the inherent variability in solar ultraviolet light, our measurements show that solar maximum varies very little across locations. Figure 2 shows measurements of solar maximum at three different locations.
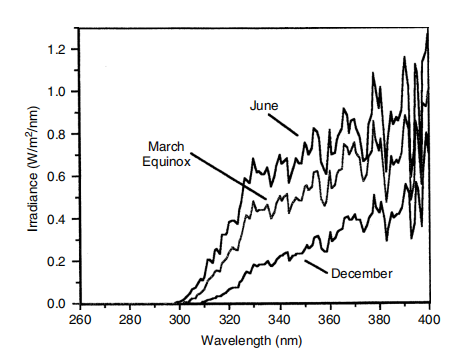
Figure 1 Seasonal variation curve of sunlight ultraviolet rays
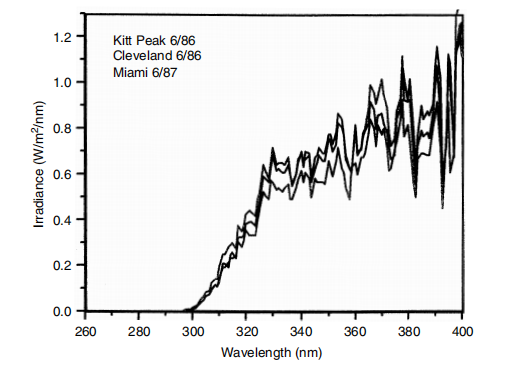
Fig.2 Solar maximum at three locations
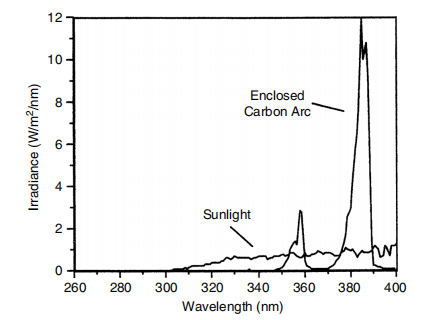
Figure 3 Closed carbon arc and sunlight
The Importance of Shortwave Cutoff
Photochemical degradation is caused by photons of light that break chemical bonds. For each type of chemical bond, there is a critical threshold wavelength of light with sufficient energy to cause a reaction. Any light with a wavelength below the threshold can break chemical bonds, but light with longer wavelengths cannot break bonds regardless of its intensity (brightness). Therefore, the importance of the short-wave cut-off of the light source is self-evident. For example, if a particular polymer is only sensitive to UV light below 295 nanometers (the sun's cutoff point), then it will not photochemically deteriorate outdoors. If the same polymer is exposed to a 280nm light source in the laboratory, it will deteriorate. While light sources that include shorter wavelengths in the spectrum yield faster tests, there is a potential for anomalous results if the Tester's wavelength cutoff is well below the material's end-use environment.






