Surface Tension

Surface tension is a property of liquids caused by unbalanced molecular cohesion at or near the surface, with the result that the surface tends to shrink and behave like a stretched elastic film. Polar liquids exhibit strong surface tension.
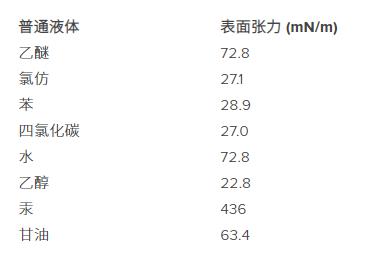
Surface tension of various air-liquid interfaces at 293 K (West, RC (Ed.)
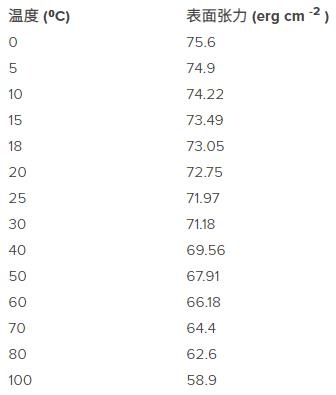
Variation of surface tension at the air-water interface with temperature (West, RC (Ed.).
Contact angle

The equilibrium contact angle of a liquid on a rigid surface, measured at the contact line where the three phases (liquid, solid, gas) within the liquid meet.
For example, a water bead on glass has a zero contact angle, but a water bead on an oily surface or plastic may have a contact angle of 90° or greater.
Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Surfaces
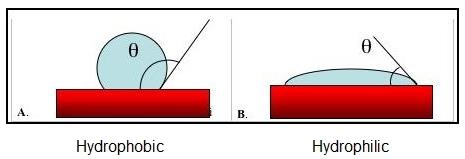
A substrate surface is said to be hydrophobic when the contact angle with water is greater than 90°. Example Figure A above.
When the contact angle with water is less than 90°, the substrate surface is said to be hydrophilic. Example Figure B above.









